Many custom options...
And formats...

Not what you want?
Try other similar-meaning words, fewer words, or just one word.
Woodblock Print Original in Chinese / Japanese...
Buy a Woodblock Print Original calligraphy wall scroll here!
Personalize your custom “Woodblock Print Original” project by clicking the button next to your favorite “Woodblock Print Original” title below...
Switched to secondary search mode due to lack of results using primary.
These secondary results may not be very accurate. Try a different but similar meaning word or phrase for better results. Or...
Look up Woodblock Print Original in my Japanese Kanji & Chinese Character Dictionary(My dictionary is a different system then the calligraphy search you just tried)
If you want a special phrase, word, title, name, or proverb, feel free to contact me, and I will translate your custom calligraphy idea for you.
1. Adventure
2. Aikikai
3. Avatar
5. Bodhidharma
8. Boxing
9. Seeing one’s Nature and becoming a Buddha
10. Bujinkan
11. Chidokan
12. Chinese Traditional Medicine
13. Christmas
15. Cuong Nhu
17. Dogen
18. Dragon Ball Kai
19. Earth
20. Eye for an eye
21. Faith is the bird that feels the light when the dawn is still dark
22. Fate / Opportunity / Chance
23. Felina / Felidae / Felinae
24. Fidelity / Personal Integrity / Honor
25. Five Elements
26. Gabriela
28. Godzilla
29. Gung Ho
30. Hidden Dragon Crouching Tiger
31. Hiro
33. Polo
35. Inner Strength is Better than Outward Appearance
36. Jada
37. Jesus
38. Christ
40. Jodi
41. John 3:16
43. Kakeru
44. Kenpo / Kempo / Quan Fa / Chuan Fa
45. Khánh
46. Meet the Buddha, Kill the Buddha
48. Kung / Gong
51. Lam
52. Lao
53. Lee / Plum
54. Life Energy / Spiritual Energy
57. Luo / Raku
58. Manga
60. Mencius
61. Moo Duk Kwan
62. Mountain Travels Poem by Dumu
63. Mumonkan / The Gateless Gate
64. Nguyen / Ruan
65. No Mind / Mushin
66. No one knows a son better than the father
67. Ono-Ha Itto-Ryu
68. Open Mind
70. Pain is Weakness Leaving the Body
71. Passions / Feelings / Emotions
72. Prosperity
74. Ramona
75. Respect
76. Ririsa
77. Ronin / Masterless Samurai
78. Sacrifice
79. Saeed
80. Sanchin
81. Sangha
82. Sasuke
83. Self Awareness Becomes a Buddha
86. Shugyo
87. Sparrow
88. Spirit / Spiritual Essence
89. Sword
90. Taekwondo
91. Taido
92. Take Refuge in the Three Treasures
93. Tan
94. Ten Commandments
95. Taekwondo Tenets / Spirit of Taekwon-do
96. Three Treasures of Buddhism
97. Thuan
98. Truong
99. Unicorn
Adventure
冒険 is a common Japanese way to say “Adventure.”
The first character can mean “to risk,” “to defy” or “to dare.” The second character means “inaccessible place” or “impregnable position.” Together, you get the idea of why these two characters mean adventure when put them together in Japanese.
Note: The second character is a morphed Japanese Kanji. The original Chinese version is also available and holds the same root meaning.
Aikikai
合気会 or “Aikikai” is the original school of Aikido.
Several organizations use this title. The first was established in Japan in 1940 (The Aikikai Foundation or 財団法人合気会).
The only difference between this title and Aikido is the last character, “kai” which means club, group, fraternity, organization, or assembly.
Note: 合気会 may be romanized with a dash like this: Aiki-Kai.
Avatar
化身 is a way to say avatar in Chinese characters, Korean Hanja, and Japanese Kanji.
This is the original Buddhist idea of an avatar (not the movie). This can also mean: incarnation; reincarnation; embodiment; personification; impersonation.
化身 is the Chinese word used for the original Sanskrit, nirmāṇakāya. Alternates for nirmāṇakāya include 應身, 應化身, or 變化身. In the context of Buddhism, this is a Buddha's metamorphosic body, which has the power to assume any shape to propagate the Truth. This title, 化身, is used for the appearance of a Buddha's many forms.
Mind of the Beginner
Shoshin
初心 is often translated in Japanese as “beginner's mind” or “beginner's spirit.”
In Chinese, the dictionary definition is “one's original intention.”
The first character means first, initial, primary, junior, beginning, or basic.
The second character means heart, mind, soul, or essence.
初心 is one of the five spirits of the warrior (budo) and is often used as a Japanese martial arts tenet. Under that context, places such as the Budo Dojo define it this way: The state of shoshin is that of a beginners mind. It is a state of awareness that always remains fully conscious, aware, and prepared to see things for the first time. The attitude of shoshin is essential to continued learning.
Bodhidharma
Body / Karada
体 is used in Japanese to mean “body.”
体 can also refer to the form, style, corporeal existence, appearance, identity, or state of something or someone. 體 is also used in Buddhism in regard to the corporeal existence of someone (their earthy vessel). It's kind of a broad term that can be used in a lot of different ways.
As a single character, it's usually pronounced “karada” but it can also be pronounced “tai” or “te” (Japanese pronunciation borrowed from the original Chinese).
體 is not a common Kanji to use for a wall scroll. Only select this if you have a personal and meaningful reason to do so. Also, consider this version to be “Japanese only” - see below...
![]() In Chinese and old Korean Hanja, this character is written in the traditional form shown to the right. If you want this version, click on the character to the right instead of the button above.
In Chinese and old Korean Hanja, this character is written in the traditional form shown to the right. If you want this version, click on the character to the right instead of the button above.
Body and Earth in Unity
身土不二 (Shindofuni) is originally a Buddhist concept or proverb referring to the inseparability of body-mind and geographical circumstances.
This reads, “Body [and] earth [are] not two.”
Other translations or matching ideas include:
Body and land are one.
Body and earth can not be separated.
Body earth sensory curation.
You are what you eat.
Indivisibility of the body and the land (because the body is made from food and food is made from the land).
Going further, this speaks of our human bodies and the land from which we get our food being closely connected. This phrase is often used when talking about natural and organic vegetables coming directly from the farm to provide the healthiest foods in Japan.
Character notes: 身(shin) in this context does not just mean your physical body but a concept including both body and mind.
土 (do) refers to the soil, earth, clay, land, or in some cases, locality. It's not the proper name of Earth, the planet. However, it can refer to the land or realm we live in.
Japanese note: This has been used in Japan, on and off, since 1907 as a slogan for a governmental healthy eating campaign (usually pronounced as shindofuji instead of the original shindofuni in this context). It may have been hijacked from Buddhism for this propaganda purpose, but at least this is “healthy propaganda.”
Korean note: The phrase 身土不二 was in use by 1610 A.D. in Korea, where it can be found in an early medical journal.
In modern South Korea, it's written in Hangul as 신토불이. Korea used Chinese characters (same source as Japanese Kanji) as their only written standard form of the language until about a hundred years ago. Therefore, many Koreans will recognize this as a native phrase and concept.
See Also: Strength and Love in Unity
Boxing
拳擊 is the term used in Chinese to refer to the original Olympic sport of combat and fighting.
If you like to strap on your boxing gloves and go a few rounds or are just a fan of boxing, this could make a nice wall scroll for you.
Note that Japanese use the same first character (which means fist) but a different Kanji for the second. Please see our Japanese boxing entry for that version.
Boxing
拳闘 is the term used in Japanese Kanji to refer to the original Olympic sport of combat and fighting.
This can also be translated as prizefighting.
The first Kanji means fist. The second means fight. So when literally translated, this means “fistfight” (though understood in Japanese as a more refined sport, versus street fighting).
Note: A completely different second character is used in the Chinese word for boxing but a Chinese person would still be able to guess the meaning of these Kanji.
Seeing one’s Nature and becoming a Buddha
見性成佛 is a universal phrase that suggests that one may see one's nature and accomplish Buddhahood.
見性 suggests penetrating deep inside oneself to see one's “Original finally
Mind.”
成佛 refers to a sentient being who dispenses with illusions and delusions
through ascetic practice, is enlightened to the truth, and becomes a Buddha.
This is used by Mahayana, Chan, and Zen Buddhists in China, Korea, and Japan.
You will also see this with the last character written as 仏 in Japanese. In the religious context, 佛 is commonly used to mean Buddha. If you want the other version, see Kenshō Jōbutsu 見性成仏
Bujinkan
Chidokan
致道館 is the name Chidokan.
Chidōkan was established in 1805. The original Chidōkan school was located in Tsuruoka, Japan.
The original school taught a combination of traditional Chinese literature, Ogasawara-ryū etiquette, Chinese medicine and martial arts alongside Confucianism.
Chinese Traditional Medicine
Christmas
聖誕 is how to write Christmas in Chinese.
The original meaning was the Emperor's Birthday (and sometimes Confucius' birthday), but in modern times, this is almost exclusively used to refer to the western religious holiday of Christmas.
Creative / Creativity
創意 is creative or creativity in Chinese characters, old Korean Hanja, and Japanese Kanji.
It can also refer to an original idea or originality.
Cuong Nhu
剛柔 is a term that means hardness and softness or hard and soft.
剛柔 is also the Chinese character origin of the martial arts style known as Cương Nhu.
Cương Nhu or Cuong Nhu was founded by Grandmaster Ngo Dong in 1965 in Hue, Vietnam, and brought to the U.S. in 1971.
剛 means hard, firm, strong, and just.
柔 means soft, flexible, supple, yielding, softness, and/or gentleness.
Until it was romanized in the mid-17th century by Portuguese missionaries with later influence by French missionaries, Vietnamese was exclusively written in Chinese characters. With some research, you can still figure out the original way to write most Vietnamese words and titles in Chinese characters. That is what I did here to figure out that Cuong Nhu would have been 剛柔 if established in ancient Vietnam.
Same characters are used in Japanese for various Goju schools of Okinawan martial arts, though not the same lineage as the Vietnamese style described above.
Death Before Dishonor
A soldier can die or kill, but never dishonor or disgrace himself
士可殺不可辱 almost directly matches the military idea of “Death Before Dishonor,” while also being an ancient Chinese proverb.
The direct meaning is, “[A] soldier/warrior can die/kill [but he/she] cannot [allow] dishonor/disgrace [upon himself/herself].” Chinese grammar, and especially ancient grammar, is a little different than English. Not nearly as many articles are needed, and a lot is implied.
There are a lot of ways to express ideas similar to “Death Before Dishonor” in Chinese, and I would rate this one in the top two.
This is the original form of this proverb with the character for “soldier/warrior” at the beginning. Most of the time, this character is dropped, becoming a five-character proverb (the soldier/warrior part is implied, even without the character being present in the proverb). We also offer a shorter version.
Dogen
Usually, when people are looking for 道元 or “Dogen,” they are referring to the Japanese Zen monk by this name.
He lived from 1200-1253. This Dogen name or title literally means “The Way Origin” or “Beginning of the Path.” It is understood to mean “beginning of right doctrine or faith” in the context of his name and work to establish the Sōtō school of Zen in Japan.
To accomplish that task, this humble monk traveled from Japan and across China to find the more original or pure forms of Buddhism.
Dragon Ball Kai
ドラゴンボール改 is the name for Doragon Bōru Kai (Dragon Ball Revised), a high-definition remastered and recut of the original Dragon Ball Z, released on the 20th anniversary.
Note: Because this selection contains some special Japanese Katakana characters, it should be written by a Japanese calligrapher.
Earth
(Used in Japanese version of five elements)
地 is the single-character element and title of the planet Earth in Chinese, old Korean Hanja, and Japanese Kanji.
Because this is a single character, the definition is a little ambiguous and can have many meanings depending on the context in which it is used. These meanings include: earth, ground, land, soil, dirt, place, territory, bottom (of a package, book, etc.), earth (one of the Japanese five elements), the region in question, the local area, skin, texture, fabric, material, weave, base, background, one's true nature, narrative (i.e. descriptive part of a story), real life, actuality, etc.
In Japanese, this Kanji can be pronounced several ways, including chi, ji, tsushi, or tsuchi.
地 is also an element of the Japanese version of the five elements (the original Chinese version uses a different version of earth).
Eye for an eye
Faith is the bird that feels the light when the dawn is still dark
信唸是在黎明前的黑闇中能感到光明的鳥 is a philosophical poem/quote from Indian Poet and Philosopher, Rabindranath Tagore.

Rabindranath Tagore, 1915
This quote is not sourced, and therefore several variations exist in English. Some suggest the original was in the Bengali language.
This, of course, is the Chinese translation that has the meaning of, “Faith is the bird that feels the light and sings when the dawn is still dark.”
More about Rabindranath Tagore
Fate / Opportunity / Chance
The Buddhist idea of Fate
因緣 is the Buddhist concept of a chance meeting or an opportunity that presents itself by fate.
Sometimes this is used to describe a cosmic chain of events or cause and effect.
It also is used to describe predestined relationships between people - and sometimes married couples (although if you want one about marriage, try this: Fate / Destiny of Lovers.
因緣 can also be translated as origin, karma, destiny, affinity, connection, and relation. This all depends on context - seen alone on a wall scroll, this will be read with a “fate/chance” meaning by a Chinese person or a Korean person who can read Hanja.
The more complex definition of this word would be, “Direct causes and indirect conditions, which underlie the actions of all things.”
This concept is known as nidana in the original Sanskrit. Also sometimes presented as hetupratyaya (or “hetu and prataya”), which I believe is Pali.
Note: Japanese will tend to use this version of the second Kanji: ![]()
If you order this from the Japanese master calligrapher, expect that you’ll get this version. However, this word often carries a negative connotation in Japanese (bad things happen), as it is used that way in a certain Japanese idiom. Therefore, this may not be the best choice if Japanese is your target language.
See Also: Buddhism | Opportunity
Felina / Felidae / Felinae
貓科 is the Chinese way to write Felidae, Felina, or Felinae (the cat family).
In Japanese, they use a slightly different first character and write 猫科, and pronounce it “nekoka” instead of the original 貓科.
Also, in Chinese, sometimes the title for the sub-family of cats is 猫亚科 for Felinae. If you need a special term, just contact me.
Fidelity / Personal Integrity / Honor
操守 is the Chinese and Japanese Kanji for personal integrity, constancy, fidelity, and honor/honour.
The original meaning of the first character is chastity, fidelity, honor, and/or faith.
The second character means to defend, guard, keep watch, and be observant.
So, this is about being observant of and guarding your integrity and honor.
Five Elements
地水火風空 is the specifically-Japanese version of the five elements.
This is a little different than the ancient or original Chinese version.
The elements are written in this order:
1. Earth / Terra / Ground
2. Water
3. Fire
4. Wind / Air
5. Sky / Emptiness / Void / Ether
Note: This set of Kanji can also be romanized as “ji sui ka fuu kuu,” “jisuikafuukuu,” or “jisuikafuku.”
These can also be written in the order 地火風水空 (chi ka sui fuu kuu). Let me know when you place your order if you want the Kanji to be in this character order.
Gabriela
Godai / Five Elements
五大 is the Japanese title for the five elements.
In Japan, the five elements differ slightly from the original Chinese. Therefore, in Japanese philosophy, you have earth, water, fire, wind, and void (space).
The meaning of the first character is 5, but the second character means great or large. Some translate this as the five majors. 大 is only understood as “elements” when you have 五 in front of it.
In Buddhism, this can be short for 五大明王, or the five great and wise kings.
Godzilla
Godzilla
呉爾羅 was one of the original ways that Godzilla was written in Japanese Kanji.
However, the characters are used for their phonetic value rather than meaning. Later, Godzilla was written in Katakana (a specifically-phonetic character set in Japan) as ゴジラ. Either way that romanizes as Gojira. The name or title Godzilla is really the English version.
Gung Ho
Working Together
工合 is one of those Asian words that is used more in English than in the original Chinese.
Gung Ho was originally used to speak of Carlson's Raiders, a group of “Gung Ho” U.S. Marines who went on an island-hopping campaign of death during WWII.
A movie called Gung Ho came out in the mid-1940s and was later re-released in the 1950s depicting the 2nd Marine Raider Battalion, and brought this word to the mainstream.
It is still sometimes used today within the U.S. Marine Corps brotherhood to refer to a unit or group that works well together or is otherwise efficient and motivated (has good morals).
In 1986, there was a movie called Gung Ho about a Japanese company taking over an American automotive factory. They completely ignored the fact that this was a Chinese title.
It should be noted that this title actually means a condition, state, manner, or the health of something in Japanese.
Language and pronunciation notes:
Like many Asian words absorbed into common use in English, this one is drastically mispronounced. The official Romanization is “gong he” but that doesn't tell you enough. The vowel sound on the first character is like the English word “own,” now just add the g-sounds to the beginning and end. The second character is misleading, as you might think it is like the English word “he.” In reality, the vowel sound is more like the “u” in “up.”
It should also be noted that the current generation in China no longer uses or recognizes this as a common word or slogan.
Note: This can be pronounced and is a word in Japanese, though seldom used. Japanese will use a variation of "具合" instead. But still, not common.
The meaning of 藏龍臥虎 is that both the tiger and dragon have amazing talents, but if they are out of view, you may not have discovered them.
This old Chinese idiom/proverb is appropriate for someone with an amazing ability that keeps that ability hidden.
You might think this title is in reverse, but actually, this is the original Chinese proverb.
The movie Crouching Tiger, Hidden Dragon, popularized this alternate version.
Hiro
広 is the Japanese variant of 廣 (from Chinese).
The original meaning is wide, numerous, or to spread out. However, in modern Japan, this is used primarily as a given name. Most often it is romanized as Hiro.
This Kanji can also romanize as the names Yutaka, Hiromu, Hiromatsu, Hirotsugu, Hirosue, Hiroji, Hiroshi, Hirosaki, Hirokatsu, Kouji, or Kou.
In Chinese, this would romanize as guǎng where it still holds the original meaning and is a common Chinese surname. However, this 広 version is strictly Japanese, and most Chinese will not realize it’s a variant of 廣. This will be true especially in the mainland where the Simplified Chinese is now written as 广.
Hon Sha Ze Sho Nen
Polo
馬球 is the Chinese title for the ancient game of polo.
During the Tang Dynasty (618-907 AD), the elite and rich would mount their horses and engage in this rigorous sport. It was the only sport of that period that women were also known to play.
The original polo came from Persia and may have been played in China hundreds of years before the Tang popularized it.
The characters “馬球” literally mean “horse ball.”
House of Red Delights
怡紅院 is from “The Story of the Stone” by Cao Xueqin.
For some reason, this phrase was translated as “House of Green Delights” when the novel was published in English. The translator took some liberties and believed that “green” had a more positive feel than red to a western audience. Therefore, the phrase shown to the right is “House of Red Delights” (which is the most original and correct way).
Inner Strength is Better than Outward Appearance
表壯不如里壯 literally translates as: [Better to be] strong inside than [to be] strong outside.
The ancient original meaning was:
[An] able [husband] outside [working to support a family is] not as good as [an] able [wife] inside [working and saving to take care of the family].
The current meaning is:
Inner strength is more important than outward appearance.
Jada
Jesus
This is simply the name “Jesus” transliterated into Chinese. 耶穌 hold a pronunciation in Mandarin that is closer to the real and original Hebrew Yeshua, instead of the incorrect way we have always pronounced Jesus in English with a hard “J” sound. While this name sounds like the real “Jesus” in Chinese, Christians in China are more likely to say “Christ” (Jidu) which holds more meaning than just sound.
If you are Latino and have been given the name “Jesus,” this is also how to write your name in Chinese.
Christ
基督 is how to write “Christ” in Chinese characters, Korean Hanja, and Japanese Kanji.
This is the word used in the Chinese Union Bible (the only readily-available translation of the Bible into Chinese that I know of - published about 100 years ago). For Chinese Christians, this is the most common way to refer to Jesus Christ.
This is also the way that “Christ” is written in Japanese. But since the Japanese language is very flexible about the sounds that can be assigned to various Kanji, these characters have been assigned a pronunciation that sounds a lot like “Christ” or actually closer to the original “Christos.” In Japanese (if you don't know how the Romaji shown above in the gray box works), it sounds like “key ree sue toe” using English words/sounds. Say those four words fast, and you'll get it.
It should be noted that only Japanese Christians will be familiar with this word.
This is best defined, read, and understood with the characters together, but if you take this word for Christ apart, the first character means “fundamentals” or “foundation.” The second character can mean “leader” or “boss.”
Jesus Christ is Love
Jodi
John 3:16
神愛世人甚至將他的獨生子賜給他們叫一切信他的不至滅亡反得永生 is the full translation of John 3:16 into Chinese.
This is from the Chinese Union Bible which comes from a revised version of the King James. This Chinese Bible was originally translated and printed in 1919 (several revisions since then).
Because of the origin being the KJV, I'll say that in English, this would be, “For God so loved the world, that he gave his only begotten Son, that whosoever believeth in him should not perish but have everlasting life.”
As with any translation, there are interesting cultural and linguistic issues. For instance, the word used for “world” in Chinese can also mean “common people.” So you could say that it means “For God so loved the common people...”
This does not take away from the text, as it will be understood with the same meaning and connotation.
There is no direct Greek-to-Chinese translation in print (that I know of), so this is the best available. Of course, you can ask any Greek person of faith, and they will claim that a bit is lost from the original Greek of the New Testament to any of the English versions of the Bible in print.
Journey to the West
西遊記 is the original title of the novel Journey to the West.
Written during the Ming dynasty, this novel by Wu Cheng'en (吳承恩) is one of the four classic stories of Chinese literature.
Sometimes this book is titled, Pilgrimage to the West, Monkey King, or Magic Monkey.
Many movies and TV series depict or adapt portions of this story.
Kakeru
Kenpo / Kempo / Quan Fa / Chuan Fa
拳法 is a form of martial arts that can be translated in several ways.
Some will call it “fist principles,” “the way of the fist,” or even “law of the fist.” The first character literally means fist. The second can mean law, method, way, principle, or Buddhist teaching.
Kempo is really a potluck of martial arts. Often a combination of Chinese martial arts such as Shaolin Kung Fu with Japanese martial arts such as Karate, Jujutsu (Jujitsu), Aikido, and others. You may see the term “Kempo Karate,” which basically means Karate with other disciplines added. In this way, Kempo becomes an adjective rather than a title or school of martial arts.
These facts will long be argued by various masters and students of Kempo. Even the argument as to whether it should be spelled “kenpo” or “Kempo” ensues at dojos around the world (the correct Romaji should actually be “kenpou” if you precisely follow the rules).
The benefit of Kempo is that the techniques are easier to learn and master than pure Kung Fu (wu shu). Students are often taught basic Karate moves, kicks, and punches before augmenting the basic skills with complex Kung Fu techniques. This allows students of Kempo to achieve a level where they can defend themselves or fight in a relatively short amount of time (a few years rather than a decade or more).
Because the definition of this word is so fluid, I should make some notes here:
1. Purists in Okinawa will claim that “Okinawa Kenpo” or “Ryukyu Hon Kenpo” is the original and true version of this martial art from the old kingdom. It is actually little or no connection between Okinawa Kenpo and the way the word is used elsewhere.
2. In Chinese, where these characters are pronounced “quan fa” (sometimes Romanized as “chuan fa” because the Chinese-pinyin “q” actually sounds like an English “ch” sound), these characters do not hold the connotation of being a mixed martial art. It is simply defined as “the law of the fist.”
3. My Japanese dictionary oddly defines Kenpo as the “Chinese art of self-defense.” I personally don't feel this is the most common way that people perceive the word but just something you should know.
Khánh
磬 means “chime stones,” but I'm including it here for those looking for the original Chinese character for the Vietnamese name Khánh.
Other definitions include ancient percussion instrument made of stone or jade pieces hung in a row and struck as a xylophone, sounding stone, ancient Chinese chime shaped like a chevron.
There is also a possibility that your original character is 慶 which means to celebrate or felicity. Contact me if you need that character.
Meet the Buddha, Kill the Buddha
This controversial Buddhist koan means “On encountering Buddha, you should kill him.”
This is the short concise Japanese version of an original statement by ninth-century Chinese Buddhist monk Linji Yixuan, “If You Meet The Buddha On The Road, Kill Him.”
This takes some explaining... The concept here is that if you think you have seen, experienced, or achieved true enlightenment, the chances that you really have are so slim that you should kill or dismiss that idea.
Another suggestion is that one's path to becoming a Buddha is one's own, and one should not get caught up in religious fervor, and avoid “showing off” that they are a Buddhist.
Helpful references for this concept:
Lion's Roar addresses "If You Meet The Buddha On The Road, Kill Him"
Kill the Buddha
Note: Because this selection contains some special Japanese Hiragana characters, it should be written by a Japanese calligrapher.
Koushinkan / Koshinkan
孝心館 is the title for Koushinkan, Koshinkan, or Kōshin-Kan.
The romanization of this title varies a little, but the original characters are the same.
孝 = Filial piety or obedience.
心 = Heart, mind, intention, or center.
馆 = Building or establishment (dojo).
This can be pronounced in Chinese and has the same meaning, but you should consider this a Japanese martial arts title.
Kung / Gong
龔 is a Chinese surname that can be romanized as Gong or Kung.
From most of China, it would be Gong, but from Cantonese, it is often romanized as Kung.
In Korean, this could be a surname that romanizes as Gong or Kong and is now written as 공.
The original meaning of the character was something like, “to provide.”
Kung Fu / Gong Fu
功夫 or Kung Fu is one of the most famous types of martial arts in the world - and not just because of Bruce Lee.
Some translate the meaning as “Accomplishment by Great Effort.” I think this is partially true, but directly translated, it literally means “Merit/Achievement/Accomplishment Man.” The word “fu” can sometimes mean “husband” or “porter,” but in this case, it can only mean “man.” However, few in China will think “man” when they hear the word “Gong Fu” spoken.
This term is also used for things other than martial arts. In fact, it's used to refer to a person with excellent skills in crafts that require a lot of effort to master, such as cooking, tea ceremonies, and calligraphy.
What a lot of people don't know is that the spelling of “Kung Fu” was actually taken from the old Wade Giles form of Romanization. Using this method, the sounds of the English “G” and “K” were both written as “K” and an apostrophe after the “K” told you it was supposed to sound like a “G.” Nobody in the west knew this rule, so most people pronounce it with a “K-sound.” And so, Gong Fu will always be Kung Fu for most westerners.
Also, just to educate you a little more, the “O” in “Gong” has a sound like the English word “oh.”
The popular Chinese dish “Kung Pao Chicken” suffers from the same problem. It should actually be “Gong Bao Chicken.”
Historical note: Many will claim that Kung Fu was invented by the monks of the Shaolin monastery. This fact is argued in both directions by scholars of Chinese history. Perhaps it is more accurate to say that the Shaolin Monks brought the original fame to Kung Fu many generations ago.
Japanese note: While most Japanese martial artists will recognize these characters, Katakana is more often used to approximate the pronunciation of "Kung Fu" with "カンフー." Some will argue as to whether this should be considered a Japanese word at all.
See Also: Bruce Lee
To Come / To Arrive
來 means to come or to arrive.
In Japanese, this can be the female given name Rai or the surnames Takagi or Kuru (and a few other rare names). Often written 来 instead of the original 來 in modern Japanese.
In the Buddhist context, this can mean the coming or refer to the future.
Lee / Plum
This is the most common Chinese character which sounds like “Lee” or “Li” and is used as a surname / family name in China.
李 actually means “Plum.” So it's really Mr. Plum and Mrs. Plum if you translated the name instead of romanizing.
This is not the only character in Chinese that can be romanized as “Lee” or “Li.” If your family name is “Lee” or “Li” please be sure this is the correct character before you order this scroll (look at your grandparents' Chinese passports or other documents if you are an ABC and are trying to create a heritage wall scroll).
Famous people with this surname include Bruce Lee (Li Xiao-Long), Minister Li Peng, and famous Tang Dynasty poet Li Bai.
In Korea, this is the original character for a surname that romanizes as “Yi.”
Note: This also one version of Lee that is a common Korean surname. However, it’s often romanized as "Yi" and sometimes as "Ri" or "Rhee."
Life Energy / Spiritual Energy
Chi Energy: Essence of Life / Energy Flow
This 氣 energy flow is a fundamental concept of traditional Asian culture.
氣 is romanized as “Qi” or “Chi” in Chinese, “Gi” in Korean, and “Ki” in Japanese.
Chi is believed to be part of everything that exists, as in “life force” or “spiritual energy.” It is most often translated as “energy flow” or literally as “air” or “breath.” Some people will simply translate this as “spirit,” but you must consider the kind of spirit we're talking about. I think this is weighted more toward energy than spirit.
The character itself is a representation of steam (or breath) rising from rice. To clarify, the character for rice looks like this: ![]()
Steam was apparently seen as visual evidence of the release of “life energy” when this concept was first developed. The Qi / Chi / Ki character is still used in compound words to mean steam or vapor.
The etymology of this character is a bit complicated. It's suggested that the first form of this character from bronze script (about 2500 years ago) looked like these samples: 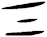
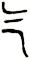
However, it was easy to confuse this with the character for the number three. So the rice radical was added by 221 B.C. (the exact time of this change is debated). This first version with the rice radical looks like this: 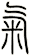
The idea of Qi / Chi / Ki is really a philosophical concept. It's often used to refer to the “flow” of metaphysical energy that sustains living beings. Yet there is much debate that has continued for thousands of years as to whether Qi / Chi / Ki is pure energy or consists partially or fully of matter.
You can also see the character for Qi / Chi / Ki in common compound words such as Tai Chi / Tai Qi, Aikido, Reiki, and Qi Gong / Chi Kung.
In the modern Japanese Kanji, the rice radical has been changed into two strokes that form an X.
![]() The original and traditional Chinese form is still understood in Japanese, but we can also offer that modern Kanji form in our custom calligraphy. If you want this Japanese Kanji, please click on the character to the right instead of the “Select and Customize” button above.
The original and traditional Chinese form is still understood in Japanese, but we can also offer that modern Kanji form in our custom calligraphy. If you want this Japanese Kanji, please click on the character to the right instead of the “Select and Customize” button above.
More language notes: This is pronounced like “chee” in Mandarin Chinese, and like “key” in Japanese.
This is also the same way to write this in Korean Hanja where it is Romanized as “gi” and pronounced like “gee” but with a real G-sound, not a J-sound.
Though Vietnamese no longer use Chinese characters in their daily language, this character is still widely known in Vietnam.
See Also: Energy | Life Force | Vitality | Life | Birth | Soul
Live Long and Prosper
The LORD is my Shepherd
耶和華是我的牧者 is the first line from Psalms 23 straight out of the Chinese Union Bible.
This reads, “The LORD is my shepherd,” or “Jehovah is my shepherd.”
The character breakdown:
耶和華 = Jehovah (most English Bibles translate as LORD or God). This Chinese title is meant to sound a bit like the original Hebrew YHWH or Yahweh.
是 = is.
我的 = my.
牧者 = shepherd.
Luo / Raku
Surname
駱 is a character that can be a Chinese surname Luo or a Japanese surname Raku.
The original meaning of this character is a camel, but that is rather archaic. The surname is the first thing that comes to mind for any Chinese or Japanese person.
Manga
漫画 is the Japanese word for cartoon, comic, caricature, or comic strip.
The older traditional form is 漫畫 and is sometimes still used in Taiwan and China (and occasionally in Japan) when referring specifically to Japanese comics.
You'll see the same 漫画 used in Mainland China as well since 画 is not just the modern Japanese form but also the Simplified Chinese version of the original 畫.
Marici / Marishiten
Mencius
孟子 is the name Mencius in Chinese.
Mencius had the name “Mèng Kē” (孟軻) at birth. This later changed to Mèng Zǐ (孟子). He lived between 372 and 289 BCE.
Mencius was a Chinese Confucian philosopher who has often been referred to as the “Second Sage” following Confucius himself.
For disambiguation, one of the classic books of Confucianism is also titled 孟子.
Romanization of Mencius from Chinese includes Meng Tsu, Mengzi, and his original name Mengke or Meng Ko. In Japanese, he is Mōshi or Moushi.
Moo Duk Kwan
武德館 is the original title for the Korean martial arts style, Moo Duk Kwan.
Mountain Travels Poem by Dumu
This poem was written almost 1200 years ago during the Tang dynasty.
It depicts traveling up a place known as Cold Mountain, where some hearty people have built their homes. The traveler is overwhelmed by the beauty of the turning leaves of the maple forest that surrounds him just as night overtakes the day, and darkness prevails. His heart implores him to stop, and take in all of the beauty around him.
First, before you get to the full translation, I must tell you that Chinese poetry is a lot different than what we have in the west. Chinese words simply don't rhyme in the same way that English or other western languages do. Chinese poetry depends on rhythm and a certain beat of repeated numbers of characters.
I have done my best to translate this poem keeping a certain feel of the original poet. But some of the original beauty of the poem in its original Chinese will be lost in translation.
Far away on Cold Mountain, a stone path leads upwards.
Among white clouds, people's homes reside.
Stopping my carriage I must, as to admire the maple forest at nights fall.
In awe of autumn leaves showing more red than even flowers of early spring.
Hopefully, this poem will remind you to stop, and “take it all in” as you travel through life.
The poet's name is “Du Mu” in Chinese that is: ![]()
![]() .
.
The title of the poem, “Mountain Travels” is: ![]()
![]()
You can have the title, poet's name, and even “Tang Dynasty” written as an inscription on your custom wall scroll if you like.
More about the poet:
Dumu lived from 803-852 AD and was a leading Chinese poet during the later part of the Tang dynasty.
He was born in Chang'an, a city in central China and the former capital of the ancient Chinese empire in 221-206 BC. In present-day China, his birthplace is currently known as Xi'an, the home of the Terracotta Soldiers.
He was awarded his Jinshi degree (an exam administered by the emperor's court which leads to becoming an official of the court) at the age of 25 and went on to hold many official positions over the years. However, he never achieved a high rank, apparently because of some disputes between various factions, and his family's criticism of the government. His last post in the court was his appointment to the office of Secretariat Drafter.
During his life, he wrote scores of narrative poems, as well as a commentary on the Art of War and many letters of advice to high officials.
His poems were often very realistic and often depicted everyday life. He wrote poems about everything, from drinking beer in a tavern to weepy poems about lost love.
The thing that strikes you most is the fact even after 1200 years, not much has changed about the beauty of nature, toils, and troubles of love and beer drinking.
Mumonkan / The Gateless Gate
無門関 is the specifically Japanese title for “The Gateless Barrier.”
This has both direct meaning and is the title of a 13th-century collection of koans, compiled by Zen Master Mumon (actually a Chinese Chan Master known as Wumen in China).
The original title is 無門關, but the last Kanji was simplified to 関 in modern Japan.
Nguyen / Ruan
Surname
阮 is the original Chinese character that represented the Vietnamese surname Nguyễn before Vietnam stopped using Chinese characters and romanized their language. It is probably the most common surname in all of Vietnam. While romanized as Nguyen, it sounds more like the English word “Win” or “When.” 阮 can also represent the Nguyen Dynasty in Vietnam, which lasted from 1802 to 1945.
阮 is also the Chinese surname Ruan, most Chinese with this surname have ancestors from a small state named Ruan during the Shang Dynasty (1600-1046 BC) located in the southeast of modern-day Gansu Province.
In Japanese, this can be the rare surnames pronounced Min, Gen, Ken, Gan, or En.
Besides a surname, this character also represents an ancient musical instrument.
No Mind / Mushin
In Japanese, 無心 means innocent or without knowledge of good and evil. It literally means “without mind.”
無心 is one of the five spirits of the warrior (budo) and is often used as a Japanese martial arts tenet. Under that context, places such as the Budo Dojo define it this way: “No mind, a mind without ego. A mind like a mirror which reflects and dos not judge.” The original term was “mushin no shin,” meaning “mind of no mind.” It is a state of mind without fear, anger, or anxiety. Mushin is often described by the phrase “Mizu no Kokoro,” which means “mind like water.” The phrase is a metaphor describing the pond that clearly reflects its surroundings when calm but whose images are obscured once a pebble is dropped into its waters.
This has a good meaning in conjunction with Chan / Zen Buddhism in Japan. However, out of that context, it means mindlessness or absent-mindedness. To non-Buddhists in China, this is associated with doing something without thinking.
In Korean, this usually means indifference.
Use caution and know your audience before ordering this selection.
More info: Wikipedia: Mushin
No one knows a son better than the father
知子莫若父 can be translated as “No one knows a son better than his father.”
This idiom is based on the idea that after spending many years together, family members know everything about each other. Better than anyone else, a father knows the qualities and shortcomings of his son.
If you are looking for something about “father and son,” this is probably the best selection.
While this is the original proverb (very old), others have been composed about various combinations of mothers, sons, daughters, and fathers. Let me know if you need a custom version.
Ono-Ha Itto-Ryu
Open Mind
The Original Mind
In Zen Buddhism, 本心 means “original mind” or “original heart,” which refers to one's Buddha-nature present from birth.
This can also be translated as true feelings, real intention, one's own heart, one's right mind, one's senses, one's conscience, or fundamental mind.
Note: 心 can mean heart or mind - thought in ancient Asia to be the same organ.
Pain is Weakness Leaving the Body
I remember this being shouted a lot during U.S. Marine Corps boot camp. 疼痛就是衰弱離你而去的時候 is how to write that phrase in Chinese. At least, this is as close as we could compose/translate it, and hold the full original meaning and connotations.
The version shown here is really, “Pain is weakness leaving your body.” Although it's said in English both ways (the or your), it works better in Chinese with “your.”
Passions / Feelings / Emotions
情 means feelings, emotions, passions, and sometimes refers to the situation you are in (with your emotions).
At least, this is the definition in Chinese and Japanese. This word is a bit stronger in Korean Hanja, where it means affection, love, compassion, sympathy, tender feelings, and emotions. Just as in Chinese and Japanese, this can also refer to your circumstances or your facts of life in Korean.
情 is also the original Korean Hanja for the surname Jeong (정).
In Japanese, this can be the surname Sei.
Prosperity
繁栄 is the same “prosperity” as the Traditional Chinese version, except for a slight change in the way the second character is written (it's the Japanese Kanji deviation from the original/ancient Chinese form).
Chinese people will still be able to read this, though you should consider this to be the Japanese form (better if your audience is Japanese).

Sometimes, the Kanji form shown to the right is used in Japanese. It will depend on the calligrapher's mood as to which form you may receive. If you have a preference, please let us know at the time of your order.
Qi Gong / Chi Kung
氣功 or Qigong is the title of a technique that is somewhere between medical practice, meditation, and in some cases, religion.
The definition is blurred depending on which school of Qigong you are following. In some cases, it is even incorporated with martial arts.
Some people (even Chinese people) mix this title with Tai Chi (Tai Qi) exercises.
Lately, in China, people will claim to practice Tai Chi rather than Qigong because the Qigong title was recently used as a cover for an illegal pseudo-religious movement in China with the initials F.G. or F.D. (I can not write those names here for fear of our website being banned in China).
You can learn those names and more here: Further info about Qigong
If you are wondering why I wrote “Qi Gong” and “Chi Kung” as the title of this calligraphy entry, I should teach you a little about the various ways in which Chinese can be Romanized. One form writes this as “Chi Kung” or “Chikung” (Taiwan). In the mainland and elsewhere, it is Romanized as “Qi Gong” or “Qigong.” The pronunciation is the same in Taiwan, mainland, and Singapore Mandarin. Neither Romanization is exactly like English. If you want to know how to say this with English rules, it would be something like “Chee Gong” (but the “gong” has a vowel sound like the “O” in “go”).
Romanization is a really confusing topic and has caused many Chinese words to be mispronounced in the west. One example is “Kung Pao Chicken,” which should actually be more like “Gong Bao” with the “O” sounding like “oh” for both characters. Neither the Romanization system in Taiwan nor the Mainland is perfect, in my opinion, and leads to many misunderstandings.
In modern Japan, you may see this written as 気功, but the original 氣功 is still recognized. If you need the Japanese version, please contact me.
Ramona
Respect
Politeness, Gratitude and Propriety
礼 is one of the five tenets of Confucius.
Beyond respect, 礼 can also be translated as propriety, good manners, politeness, rite, worship, or an expression of gratitude.
We show respect by speaking and acting with courtesy. We treat others with dignity and honor the rules of our family, school, and nation. Respect yourself, and others will respect you.
 Please note that Japanese use this simplified 礼 version of the original 禮 character for respect. 礼 also happens to be the same simplification used in mainland China. While 禮 is the traditional and original version, 礼 has been used as a shorthand version for many centuries. Click on the big 禮 character to the right if you want the Traditional Chinese and older Japanese versions.
Please note that Japanese use this simplified 礼 version of the original 禮 character for respect. 礼 also happens to be the same simplification used in mainland China. While 禮 is the traditional and original version, 礼 has been used as a shorthand version for many centuries. Click on the big 禮 character to the right if you want the Traditional Chinese and older Japanese versions.
This is also a virtue of the Samurai Warrior
See our page with just Code of the Samurai / Bushido here
See Also: Confucius
Ririsa
リリサ is the name Ririsa in Japanese Katakana.
This would be the western name Ririsa in Japanese. If you are looking for the original Japanese name, it will be different (search our dictionary for that - as there are at least 10 variations that romanize as a Japanese female given name Ririsa).
Note: Because this title is entirely Japanese Katakana, it should be written by a Japanese calligrapher.
Ronin / Masterless Samurai
The 浪人 or Ronin have no master - The most famous are the 47 ronin created after their Lord committed suicide. This term was not a positive title for the Samurai of ancient Japan. However, in recent years, movies and video games have glorified the term Ronin.
In Chinese, this term has the original meaning of a hobo, vagabond, or ruffian.
In Korean Hanja, these characters would be read as adventurer, wanderer, someone without a steady job, or someone who is wasting away time.
In modern Japan, this term is used as a nickname for a high school student who has failed a college entry exam (and is trying again).
In Chinese and Korean, the Japanese definition of “Masterless Samurai” is known because of the historical context. Even in Japanese, the literal translation is closer to the Chinese and Korean definitions shown above.
This will make a fine wall scroll if you are a fan of the Ronin or see yourself as a Ronin of sorts. However, please think twice before getting a Ronin tattoo!
Sacrifice
犧牲 means sacrifice in Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and old Korean Hanja.
There is a suggestion in this word that this regards sacrificing your life.
Note: Depending on the context, this can also mean victim or scapegoat in Japanese.
In original and ancient Chinese, this word referred to sacrificial animals. It can still have this meaning in a Buddhist context.
![]() The version of the first character used in modern Japan looks like the image to the right. If you order this from the Japanese master calligrapher, it will be written in this Japanese version.
The version of the first character used in modern Japan looks like the image to the right. If you order this from the Japanese master calligrapher, it will be written in this Japanese version.
Saeed
Sanchin
三戦 is a title that literally means “three battles/conflicts/wars.”
三戦 is often figuratively used to relay the idea of a battle to unify the mind, body, and spirit.
Original usage likely comes from Fujian province in Southern China (just across from Taiwan).
This title is used in various schools such as Okinawan Karate, Uechi-Ryū, Gōjū-Ryū, Fujian White Crane, and Five Ancestors among others.
Sangha
In Buddhism, 僧伽 refers to a community of monks and/or nuns (one of the “Three Jewels”). In general terms, it can simply mean “all followers of the Buddha.”
Notes: Though there are not vast numbers of Chinese Hindus, in the Hindu faith, this term means “community together.”
The original Sanskrit word is also Romanized as samgha.
The first character means “monk.” The second character means Buddha or Shakyamuni.
僧伽 is a transliteration of the original Sanskrit, but it uses two very profound Chinese characters related to Buddhism.
Some may pronounce this as “seng qie” or “seng jia” in Mandarin (two possible pronunciations for the second character). Note that “qie” sounds like “chee-ah” using typical English pronunciation. Chinese Romanization is not actually designed to match English sounds.
![]()
![]() Note that when writing this as Kanji, Japanese will tend to write the first character in the form shown to the right. If you select our Japanese master calligrapher, please expect this special Kanji form. However, it should also be noted that this is not a common term in Japanese (except by certain sects of Buddhism or perhaps devout Buddhists in Japan).
Note that when writing this as Kanji, Japanese will tend to write the first character in the form shown to the right. If you select our Japanese master calligrapher, please expect this special Kanji form. However, it should also be noted that this is not a common term in Japanese (except by certain sects of Buddhism or perhaps devout Buddhists in Japan).
Sasuke
サスケ is the Japanese title of the TV show, Sasuke Rising.
サスケ is the original Japanese TV show that inspired the American Ninja Warrior, Ninja Warrior UK, and other variations.
It should be noted that in Japan, the show's title is usually displayed in capital Roman letters as “SASUKE,” rather than the Japanese text, サスケ. Although, both titles are known in Japan (you'd probably need to search for サスケ if looking to buy a Sasuke DVD in Japan).
Notes: Sasuke can also be a given name (written the same way). There are also other names that romanize as Sasuke in Japanese.
Note: Because this title is entirely Japanese Katakana, it should be written by a Japanese calligrapher.
Self Awareness Becomes a Buddha
自性覚れば即ち是れ佛なり is a Zen quote that means “If one realizes one's own nature, one becomes a Buddha.”
The inference here is that if you understand who you really are, and become truly aware of yourself and your original nature, you are well on your way to becoming a liberated person (a Buddha).
Note: Because this selection contains some special Japanese Hiragana characters, it should be written by a Japanese calligrapher.
Serenity / Tranquility
靜穏 is a Japanese-specific way to express “serenity” or “tranquility.”
Notes: The second Kanji is not a Chinese character - it was morphed or developed in Japan after Chinese characters were absorbed into the Japanese language during the 5th century.
The first character is slightly-simplified from the original Chinese form but still recognizable.
See Also: Peace
Shorinji Kempo / Kenpo
少林寺拳法 is a specific type of martial art in Japan that claims origins in the Kung Fu practiced in the original Shaolin Monastery of China.
The first three characters mean “Shaolin Monastery,” and you might notice the Japanese is pronounced in a very similar way. The reason is, many words were “borrowed” from the original Chinese when Japan did not have a written language and simply absorbed Chinese characters into their language around the 5th century. When a Japanese word did not exist, the Chinese pronunciation was often absorbed as well as the written form.
The last two characters mean “fist law” or “method of the fist.” It has long been argued as to whether the Japanese for these characters should be Romanized as “kempo” or “kenpo.” The official method should be “kenpou” but it's common to drop the “u” that comes after the “o.”
I imagine if you are looking for this title, you already know what it means, so the above is simply extra information that a student of Shorinji Kempo might want to know.
Shugyo
修行 is shugyō or shugyou in Japanese. It refers to ascetic practices, training, practice, discipline, and study.
修行 is also a word in the original Chinese, referring more to religious studies and practices.
In the Buddhist context, this represents caryā. In Buddhism, this relates to one's conduct, observing and doing, cultivating oneself in the right practice, and/or being pious.
Sparrow
麻雀 is the common and specific name for a hemp sparrow bird in Chinese.
This was also the original name for the game, known commonly as Mahjong. You will still see boxes of Mahjong tiles with the title 麻雀 for sparrow instead of the modern 麻將 in Southern China. This title is also used for Mahjong in Japan.
Spirit / Spiritual Essence
神 is the simplest way to write spirit in Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and old Korean.
This single character alone will conjure up ideas of the spiritual world. 神 can also be translated as “vital awareness” as in the fact that one must know they exist to exist (I think, therefore, I am).
Other translations include:
God, deity, mysterious, divine essence, lively, spiritual being, divinity, supernatural, soul, mind, nerves, and energy. In some extended context, it can mean genius or unusual.
Japanese romanizations vary a lot when this character is combined into other words. However, shin is the original pronunciation taken from Chinese into Japanese. You'll also see it romanized as kami, gami, jin, and a few others, depending on context.
Sword
剱 is the modern Japanese way to write sword.
This Kanji character comes from original Chinese. This form would also be understood in Chinese (there are often several ways to write the same character) but I suggest this one only if your audience is Japanese (because they've settled on a slightly different form as the standard in China).
In Japanese, this character also means saber/sabre, blade, bayonet, stinger, and clock hand (clock hands are the “swords” of the clock).
See Also: Katana
Taekwondo
跆拳道 is one of the most widespread types of martial arts in the world as well as being an Olympic sport. Taekwondo was born in Korea with influences of Chinese and Japanese styles combined with traditional Korean combat skills. Some will define it as the “Korean art of empty-handed self-defense.”
In the simplest translation, the first character means “kick,” the second character can mean either “fist” or “punching,” and the third means “way” or “method.” Altogether, you could say this is the “Kick Punch Method.” When heard or read in various Asian languages, all will automatically think of this famous Korean martial art. It is written the same in Japanese Kanji, Chinese, and Korean Hanja characters - so the appearance of the characters is universal. However, you should note that there is another way to write this in modern Korean Hangul characters, which looks like the image to the right. 
We suggest the original Korean Hanja (Chinese characters) for a wall scroll, but if you need the Hangul version, you must use master calligrapher Cao Bin: Order Taekwondo in Korean Hangul
Note: Taekwondo is sometimes Romanized as Tae-Kwondo, Tae Kwon Do, Taekwon-do, Taegwondo, Tae Gweon Do, Tai Kwon Do, Taikwondo, Taekwando, Tae Kwan Do and in Chinese Taiquandao, Tai Quan Dao, Taichuando, or Tai Chuan Tao.
Taido
Taidō (The Way of the Body) is a style of Karate practiced in Japan and popular worldwide.
Taidō or 躰道 traces a lineage from Genseiryū (玄制流), which came from Shuri-te (首里手), one of the original martial arts schools of ancient Okinawa.
The first character 躰 is a variant of the original Chinese character 體. In modern Japan, they tend to use 体, a more simple character form. 体 is also the modern Simplified Chinese form of 體.
The 躰 character is correct for this 躰道 martial arts title. But it can be confusing with so many variants out there, not to mention other homophonic Japanese words that also romanize as Taidō or Taidou.
To have a bit more fun with this 躰 character, it has a 身 radical on the left, which sets it apart. The meaning doubles up on the “body” as 身 (shin) is a character that also means body in Japanese and Chinese. On the right is 本, which often means root, stem, origin, source, or fundamental (but can also mean “book” in some contexts). This has deviated from the original 體 which was 骨 (bone) + 豊 (vessel). Hence, the body was your “bone vessel” in ancient Asia.
The meaning of 躰, as well as 體 and 体, is usually translated as the body. When related to the physical body, it can also refer to the torso, trunk, build, physique, or the constitution of a person. As an extension of this, it can also refer to someone's health (good body = good health).
However, depending on the context, it can encompass other meanings such as form, style, system, experience, aspect, corpus, corporeal, substance, or essentials.
The second character, 道, is recognized and well-known as the “Way” and is the same “do” as in Karate-do or Aikido.
Take Refuge in the Three Treasures
Tan
Surname
譚 is the surname Tan in Chinese.
The original form is 譚 but generations ago some changed the character to 覃 and some write it 檀 or 談. All of these romanize as tán in Mandarin Chinese and Tam in Cantonese. 覃, 檀, and 談 are rarely used for surnames now, you probably want 譚.
If you are looking for the origin of the Vietnamese name Tan, that came from 秦.
If you need one of these other characters, just copy and paste it into the search bar above, and an "Order Scroll" button will appear for you.
Ten Commandments
十戒 means Ten Commandments or Ten Precepts.
In the Buddhist context, these are prohibitions consisting of five commandments for the layman:
1. Not to destroy life 不殺生 Pāṇātipātāveramaṇi.
2. Not to steal 不倫盜 Adinnādānāver.
3. Not to commit adultery 不婬慾 Abrahmacaryaver.
4. Not to lie 不妄語 Musāvādāver.
5. Not to take intoxicating liquor 不飮酒 Suramereyya-Majjapamādaṭṭhānāver.
The ten commandments for the monk are the preceding five plus:
6. Not to eat food outside of regulated hours 不非時食 Vikāla-Bhojanāver.
7. Not to use garlands or perfumes 不著華鬘好香塗身 Mālā- Gandha-Vilepana-Dhāraṇa-Maṇḍana-Vibhūṣanaṭṭhānā.
8. Not to sleep on high or broad beds (chastity) 不坐高廣大牀 Uccāsayanā-Mahāsayanā.
9. Not to take part in singing, dancing, musical or theatrical performances 不歌舞倡伎不往觀聽 Nacca-Gīta-Vādita-Visūkadassanāver.
10. To refrain from acquiring uncoined or coined gold, or silver, or jewels 不得捉錢金銀寶物 Jātarūpa-Rajata-Paṭīggahaṇāver.
These original Buddhist commandments date back to about 2500 years ago. The English definitions above are followed by Chinese characters and original Pali pronunciation.
Under the Māhayāna Buddhism, these ten commands for the monk were changed, to accord with the new environment of the monk, to the following: not to kill, not to steal, to avoid all unchastity, not to lie, not to slander, not to insult, not to chatter, not to covet, not to give way to anger, to harbor no skepticism.
Taekwondo Tenets / Spirit of Taekwon-do
跆拳道精神禮義廉耻忍耐克己百折不屈 is General Choi's writing that is often called “The Tenets of Taekwon-do.”

The actual title would be translated as “Taekwondo Spirit” or “The Spirit of Taekwondo.” It was originally written in Korean Hanja (Chinese characters used in Korea for about 1600 years).
General Choi's original calligraphy is shown to the right. Your custom calligraphy will be unique, and not an exact match, as each calligrapher has their own style.In modern times, the common form of written Korean is Hangul (a phonetic character set). The table below shows the text in Hangul and Hanja along with a pronunciation guide and a brief English translation:
| Traditional Korean Hanja | Modern Korean Hangul | Pronunciation | English |
| 跆拳道精神 | 태권도정신 | tae gweon do jeong sin | Taekwondo Spirit |
| 禮儀 | 예의 | ye yi | Courtesy / Etiquette / Propriety / Decorum / Formality |
| 廉耻 | 염치 | yeom ci | Integrity / Sense of Honor |
| 忍耐 | 인내 | in nae | Patience / Perseverance / Endurance |
| 克己 | 극기 | geug gi | Self-Control / Self-Denial / Self-Abnegation |
| 百折不屈 | 백절불굴 | baeg jeor bur gur | Indomitable Spirit (Undaunted even after repeated attacks from the opponent) |
| Note that the pronunciation is the official version now used in South Korea. However, it is different than what you may be used to. For instance, “Taekwon-do” is “tae gweon do.” This new romanization is supposed to be closer to actual Korean pronunciation. | |||
Three Treasures of Buddhism
The Triple Gem
三寶 is the title for “Three Precious Treasures of Buddhism” or “The Triple Gem.”
These three treasures are the Buddha 佛, the Dharma 法 (teachings or the law of the Buddha), and the Sangha 僧 (the community of monks or followers).
This term is used by most (perhaps not all) Buddhists in China, Japan, and South Korea (written the same in the original form but pronounced differently in each language). Non-Buddhists may just read this as “Three Treasures” without the religious context. For instance, there is also a “Three Treasures of Chinese Medicine” that is sometimes titled the same way.
In modern Japanese and Simplified Chinese, this is written 三宝 instead of 三寶.
Thuan
This is a Vietnamese surname Thuan, written here in the original Chinese character.
The meaning is to obey, to follow, favorable, comply, yield, or agreeable.
Truong
Unicorn
一角獣 is the Japanese name for the western unicorn (a horse with a spiral horn emerging from the head). This can also refer to a narwhal, depending on context.
一角獣 is an unusual title for a Japanese wall scroll but it's OK if you really love unicorns.
Japanese have their own ancient unicorn-like creature called a “kirin” (or qilin in the original Chinese).
This in-stock artwork might be what you are looking for, and ships right away...
Gallery Price: $200.00
Your Price: $79.88
Gallery Price: $108.00
Your Price: $59.88
Gallery Price: $108.00
Your Price: $59.88
Beauties Of The East Japanese Woodblock Repro Print Wall Scroll
Discounted Blemished
Gallery Price: $87.50
Your Price: $49.00
Gallery Price: $117.00
Your Price: $64.88
Gallery Price: $108.00
Your Price: $59.88
Gallery Price: $45.00
Your Price: $25.00
Gallery Price: $108.00
Your Price: $59.88
Gallery Price: $108.00
Your Price: $59.88
Gallery Price: $108.00
Your Price: $59.88
Gallery Price: $108.00
Your Price: $59.88
Gallery Price: $90.00
Your Price: $49.88
Successful Chinese Character and Japanese Kanji calligraphy searches within the last few hours...























































































































