Many custom options...
And formats...

Qi Gong in Chinese / Japanese...
Buy a Qi Gong calligraphy wall scroll here!
Personalize your custom “Qi Gong” project by clicking the button next to your favorite “Qi Gong” title below...
Qi Gong / Chi Kung
氣功 or Qigong is the title of a technique that is somewhere between medical practice, meditation, and in some cases, religion.
The definition is blurred depending on which school of Qigong you are following. In some cases, it is even incorporated with martial arts.
Some people (even Chinese people) mix this title with Tai Chi (Tai Qi) exercises.
Lately, in China, people will claim to practice Tai Chi rather than Qigong because the Qigong title was recently used as a cover for an illegal pseudo-religious movement in China with the initials F.G. or F.D. (I can not write those names here for fear of our website being banned in China).
You can learn those names and more here: Further info about Qigong
If you are wondering why I wrote “Qi Gong” and “Chi Kung” as the title of this calligraphy entry, I should teach you a little about the various ways in which Chinese can be Romanized. One form writes this as “Chi Kung” or “Chikung” (Taiwan). In the mainland and elsewhere, it is Romanized as “Qi Gong” or “Qigong.” The pronunciation is the same in Taiwan, mainland, and Singapore Mandarin. Neither Romanization is exactly like English. If you want to know how to say this with English rules, it would be something like “Chee Gong” (but the “gong” has a vowel sound like the “O” in “go”).
Romanization is a really confusing topic and has caused many Chinese words to be mispronounced in the west. One example is “Kung Pao Chicken,” which should actually be more like “Gong Bao” with the “O” sounding like “oh” for both characters. Neither the Romanization system in Taiwan nor the Mainland is perfect, in my opinion, and leads to many misunderstandings.
In modern Japan, you may see this written as 気功, but the original 氣功 is still recognized. If you need the Japanese version, please contact me.
Three Treasures of Chinese Medicine
精, 氣, 神 are the characters jing, qi, and shen.
As a set, these three characters are known in English as the treasures of traditional Chinese medicine, the treasures of Qi Gong, or the three treasures of Taoism / Daoism.
Sometimes this set is titled 三寶 (sānbǎo) or “three treasures,” but here, we're writing each treasure out.
Here's how these characters are perceived in this context...
Jing: nutritive essence; refined; perfected; pure
Qi: vitality; energy; force; breath; vigor
Shen: spirit; soul; mind; being
To keep it simple, you can use “essence, vitality, and spirit” to define these.
Sit Quietly in Meditation
A state of mind
入靜 is used in Taoism and Qi Gong to describe the state you can reach while sitting quietly in meditation. It contains the idea of achieving a highly-tranquil and peaceful state. Some may describe this state as “sleeping while still awake.”
If you have a relaxation or meditation room, this is the calming wall scroll that you would want hanging in that room.
Life Energy / Spiritual Energy
Chi Energy: Essence of Life / Energy Flow
This 氣 energy flow is a fundamental concept of traditional Asian culture.
氣 is romanized as “Qi” or “Chi” in Chinese, “Gi” in Korean, and “Ki” in Japanese.
Chi is believed to be part of everything that exists, as in “life force” or “spiritual energy.” It is most often translated as “energy flow” or literally as “air” or “breath.” Some people will simply translate this as “spirit,” but you must consider the kind of spirit we're talking about. I think this is weighted more toward energy than spirit.
The character itself is a representation of steam (or breath) rising from rice. To clarify, the character for rice looks like this: ![]()
Steam was apparently seen as visual evidence of the release of “life energy” when this concept was first developed. The Qi / Chi / Ki character is still used in compound words to mean steam or vapor.
The etymology of this character is a bit complicated. It's suggested that the first form of this character from bronze script (about 2500 years ago) looked like these samples: 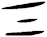
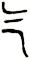
However, it was easy to confuse this with the character for the number three. So the rice radical was added by 221 B.C. (the exact time of this change is debated). This first version with the rice radical looks like this: 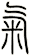
The idea of Qi / Chi / Ki is really a philosophical concept. It's often used to refer to the “flow” of metaphysical energy that sustains living beings. Yet there is much debate that has continued for thousands of years as to whether Qi / Chi / Ki is pure energy or consists partially or fully of matter.
You can also see the character for Qi / Chi / Ki in common compound words such as Tai Chi / Tai Qi, Aikido, Reiki, and Qi Gong / Chi Kung.
In the modern Japanese Kanji, the rice radical has been changed into two strokes that form an X.
![]() The original and traditional Chinese form is still understood in Japanese, but we can also offer that modern Kanji form in our custom calligraphy. If you want this Japanese Kanji, please click on the character to the right instead of the “Select and Customize” button above.
The original and traditional Chinese form is still understood in Japanese, but we can also offer that modern Kanji form in our custom calligraphy. If you want this Japanese Kanji, please click on the character to the right instead of the “Select and Customize” button above.
More language notes: This is pronounced like “chee” in Mandarin Chinese, and like “key” in Japanese.
This is also the same way to write this in Korean Hanja where it is Romanized as “gi” and pronounced like “gee” but with a real G-sound, not a J-sound.
Though Vietnamese no longer use Chinese characters in their daily language, this character is still widely known in Vietnam.
See Also: Energy | Life Force | Vitality | Life | Birth | Soul
Tai Chi Ball
This in-stock artwork might be what you are looking for, and ships right away...
Gallery Price: $200.00
Your Price: $79.88
Gallery Price: $200.00
Your Price: $79.88
Gallery Price: $200.00
Your Price: $79.88
Gallery Price: $200.00
Your Price: $79.88
Not the results for qi gong that you were looking for?
Below are some entries from our dictionary that may match your qi gong search...
| Characters If shown, 2nd row is Simp. Chinese |
Pronunciation Romanization |
Simple Dictionary Definition |
氣功 气功 see styles |
qì gōng qi4 gong1 ch`i kung chi kung |
More info & calligraphy: Qi Gong / Chi Kung |
気功 see styles |
kikou / kiko きこう |
breathing exercise; breath control; spirit cultivation; chi kung; qigong |
氣場 气场 see styles |
qì chǎng qi4 chang3 ch`i ch`ang chi chang |
qi field (in qigong or feng shui); vibe (of a person or place); aura; atmosphere |
八段錦 八段锦 see styles |
bā duàn jǐn ba1 duan4 jin3 pa tuan chin |
eight-section brocade, a traditional eight-part sequence of qigong exercises |
気功師 see styles |
kikoushi / kikoshi きこうし |
qigong therapist |
Variations: |
kikou / kiko きこう |
breathing exercise; breath control; spirit cultivation; chi kung; qigong |
全日本少林寺気功協会 see styles |
zennihonshourinjikikoukyoukai / zennihonshorinjikikokyokai ぜんにほんしょうりんじきこうきょうかい |
(org) All Japan Shaolin Temple Qigong Association; (o) All Japan Shaolin Temple Qigong Association |
The following table may be helpful for those studying Chinese or Japanese...
| Title | Characters | Romaji (Romanized Japanese) | Various forms of Romanized Chinese | |
| Qi Gong Chi Kung | 氣功 气功 | ki kou / kikou / ki ko | qì gōng / qi4 gong1 / qi gong / qigong | ch`i kung / chikung / chi kung |
| Three Treasures of Chinese Medicine | 精氣神 精气神 | jīng qì shén jing1 qi4 shen2 jing qi shen jingqishen | ching ch`i shen chingchishen ching chi shen |
|
| Sit Quietly in Meditation | 入靜 入静 | rù jìng / ru4 jing4 / ru jing / rujing | ju ching / juching | |
| Life Energy Spiritual Energy | 氣 气 / 気 | ki | qì / qi4 / qi | ch`i / chi |
| Tai Chi Ball | 太極球 太极球 | tai kyoku kyuu taikyokukyuu tai kyoku kyu | tài jí qiú tai4 ji2 qiu2 tai ji qiu taijiqiu | t`ai chi ch`iu taichichiu tai chi chiu |
| In some entries above you will see that characters have different versions above and below a line. In these cases, the characters above the line are Traditional Chinese, while the ones below are Simplified Chinese. | ||||
Successful Chinese Character and Japanese Kanji calligraphy searches within the last few hours...























