Many custom options...
And formats...

Correct in Chinese / Japanese...
Buy a Correct calligraphy wall scroll here!
Personalize your custom “Correct” project by clicking the button next to your favorite “Correct” title below...
2. Seichusen
3. Thibaud
5. Harimaya
6. Sachi
7. Miyamoto
8. Shaina
9. Yoshida
10. Itosu
11. Phan
12. Under the Protection of the Dragon Saint
13. Akari
14. Shugami
16. Live For The Day
17. 1. Right Understanding / Right Perspective / Right View / Perfect View
18. Tomika
19. Seido Juku
20. Hau
21. How can you catch tiger cubs without entering the lair of the tiger?
23. Chiu
24. Trust in God / In God We Trust
25. Kodokan
26. Yoko / Brilliant / Glorious
27. Opportunity
28. Asian Pride / Oriental Pride / AZN Pryde
29. Shoshin-Ryu
30. Success
31. Naruto
33. Strong Hearted / Strong Willed
34. Kodokan
35. Ten perfect Mahayana rules
36. The Saint
37. Bonsai / Penzai
38. Five Elements Tai Chi Fist
39. Live Strong
40. Jin Shin Jyutsu
41. Lee
42. Ninja
44. Devotion / Dedication / Attentive / Focused
45. Justice / Rectitude / Right Decision
47. Sword
48. Taido
50. Crisis equals Danger plus Opportunity?
51. Kenpo / Kempo / Quan Fa / Chuan Fa
53. Shobo
Correct and Proper
正確 is the Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and old Korean Hanja for a word meaning correct, proper, accurate, punctual, exact, authentic, or veracious.
Seichusen
This is Seichusen, the Japanese martial arts concept meaning “right/correct middle/center line/thread.”
Thibaud
Moral Principles Of Life
Harimaya
Japanese Surname
Sachi
Miyamoto
Shaina
Yoshida
Itosu
Phan
Under the Protection of the Dragon Saint
神龍庇護 is not the most common thing to say in Chinese, but it is grammatically correct and a cool title.
The first character means “supernatural or saintly.” The second is “dragon.” The last two mean protection. You could also translate this as something like “Protected by the Dragon God” or more closely “Holy Dragon.”
Akari
あかり is one of many Japanese names that romanize as Akari.
あかり is a female given name that is popular in Japan. Be sure you are ordering the correct name, as there are at least 22 variations or ways to write Akari.
Note: Because this title is entirely Japanese Hiragana, it should be written by a Japanese calligrapher.
Shugami
Abundance and Prosperity
繁榮富裕 is a proverb about “Prosperity and Abundance.”
This presents and reinforces the ideas of being prosperous, a booming economy, well-to-do, well-off, wealthy, riches, and opulence.
While this is the ancient/traditional Chinese way to write this, most Japanese can fully read and understand it. It's also the correct form of old Korean Hanja (though few Koreans of the current generation will be able to read this).
See Also: Good Fortune
Live For The Day
活在今天 is not an eastern concept, so it does not translate into a phrase that seems natural on a wall scroll.
However, if this is your philosophy, the characters shown here do capture your idea of living for today or living in the moment. 活在今天 says “Live in today,” and they are grammatically correct in Chinese.
Note: This kind of makes sense in Korean Hanja but the grammar is Chinese, so it’s not that natural in Korean.
1. Right Understanding / Right Perspective / Right View / Perfect View
Samyag Dristhi / Samyag Drsti / Samma Ditthi
正見 is one of the Noble Eightfold Paths of Buddhism. Right View, along with the Right Thought, constitutes the path to Wisdom.
To get to the correct view of the world, you must first understand and follow Four Noble Truths.
Note: This term is exclusively used by devout Buddhists. It is not a common term, and is remains an unknown concept to most Japanese and Chinese people.
See Also: Buddhism | Enlightenment | Noble Eightfold Path
Tomika
トミカ is the name Tomika in Japanese (Katakana).
This is the way to write the English name Tomika, but Tomika can also be a native Japanese name. However, there are tons of ways to write Tomika in Japanese Kanji. Please make sure you are selecting the correct one.
Note: Because this title is entirely Japanese Katakana, it should be written by a Japanese calligrapher.
Seido Juku
How can you catch tiger cubs without entering the lair of the tiger?
Nothing ventured, nothing gained
While perhaps no longer politically correct, this Chinese proverb is a reminder that you must take risks if you want rewards.
不入虎穴焉得虎子 is similar to the English proverb, “Nothing ventured, nothing gained.”
The literal word order of the Chinese is, “If (you) don't enter the tiger's lair/cave, how can (you) get/obtain tiger cubs?.”
House of Red Delights
怡紅院 is from “The Story of the Stone” by Cao Xueqin.
For some reason, this phrase was translated as “House of Green Delights” when the novel was published in English. The translator took some liberties and believed that “green” had a more positive feel than red to a western audience. Therefore, the phrase shown to the right is “House of Red Delights” (which is the most original and correct way).
Chiu
邱 is the most common Chinese character for a surname that romanizes as Chiu in Cantonese.
The surname Chiu (邱) is a common Chinese family name, especially prominent in Cantonese, Hokkien, and Taiwanese communities. However, this romanization can also come from several different Chinese surnames like Qiū (丘), Zhōu (周), Zhào (趙), and Jiāng (蔣), depending on original dialect and geography. Please confirm that this is the correct character before ordering.
Trust in God / In God We Trust
相信上帝 means exactly what the title suggests. The first two characters mean “trust” or “believe,” and the second two mean “God” (as in the God of Abraham and the God of Zion).
Thisis also how the American phrase “In God We Trust” as seen on U.S. Currency would be translated into Chinese. It would also be correct to say that this means “Believe in God,” though, in this arrangement/context, one would be more likely to interpret it as “trust.”
Kodokan
光道館 is Kodokan.
This is the title of an Aikido dojo, studio, or hall.
Be careful in selecting the correct Kodokan, as there are a few different titles that romanize as Kodokan.
Here's how the characters break down in meaning for this one:
1. Light / Bright
2. Way / Path (the Tao/Dao as in Taoism/Daoism)
3. Schoolroom / Building / Establishment / Mansion / Hall (of learning)
Altogether, you get something like “The Path of Light Establishment.”
Yoko / Brilliant / Glorious
燿 means brilliant or glorious in Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and old Korean Hanja.
I am listing this character as it is a common Japanese given name that is romanized as Yoko or Youkou. It can be romanized as these names as well: Yo, Teru, and Akira.
As with most Japanese names, this is not the only character or only name that romanizes as Yoko. Be sure you are getting the correct character before you order.
Opportunity
機 is an odd one - I've seen this on coffee cups and posters with the meaning of “opportunity.”
機 is a correct definition but this character also means “machine.” In fact, if you put the character for “flying” in front of this character, you have the Chinese word for “airplane” (literally: flying machine). Alone, on a wall scroll, it will be generally understood as “opportunity” but I want you to know this extra information before you make your selection. Note that in Japanese and Korean, this has a similar meaning but can also mean machine or loom.
See Also: Success
Asian Pride / Oriental Pride / AZN Pryde
東方自尊 is the universal way to write “Asian Pride.”
We worked on this one for a long time. The effort involved both Chinese and Japanese translators and lengthy discussions. If you have been searching for this term, there is a reason that it's hard to find the way to write “Asian Pride” in Chinese and Japanese - it's because of the inherent difficulties in figuring out a universal combination of characters that can be read in all languages that use forms of Chinese characters.
This final solution that you see to the left creates a reasonable title in Chinese and an exotic (perhaps unusual) title in Japanese (This could be read as “Eastern Self-Respect” in Japanese”).
Although not as natural, it does have the same meaning as Korean Hanja, and the older generation of Vietnamese people will be able to read it.
The first two characters literally mean “Oriental” and the second two mean “pride,” “self-esteem,” or “self-respect” (we chose the most non-arrogant way to say “pride”). If you have “Asian Pride” (sometimes spelled Asian Pryde) these are the characters for you.
Note: For those who wonder, there is nothing technically wrong with the word “Oriental.” It is a correct word, and any bad meanings were created by so-called “Asian Americans” and Caucasians in the United States. To say “Asian” would not completely correct the intended meaning since that would include people from Saudi Arabia, Iraq, Iran, India, and portions of Russia.
For further proof, if you were of East Asian ancestry and born in England, you would be known as a “British Oriental” (The “Oriental stigma” is basically an American creation and, therefore, applies mainly to the American English language - where they get a bit overzealous with political correctness).
Further, since the Chinese and Japanese word for Oriental is not English, they can not be construed as having ill meaning. On one trip to China or Japan, you will find many things titled with these two characters, such as malls, buildings, and business names. These places also use “Oriental” as their English title (much as we do since our Chinese business name starts with these same two characters).
In short, the first two characters have the meaning that Americans attach to “Asian” but is more technically correct.
Shoshin-Ryu
正心流 is a Japanese title that means “right heart style,” “true mind method,” or “truthful heart school.”
The first character means right, correct, greater, or true.
The second character means heart, mind, soul, or essence.
The third character means style, method, or some will translate it as a school.
Please note, there is more than one martial arts school that romanizes as Shoshin-Ryu.
Success
This Chinese and Japanese word for “success” is often used to refer to “career success” but is also used for other successes in life.
It matches the western dictionary definition of “The achievement of something desired, planned, or attempted.” And It's also used in this old Chinese proverb:  which means Failure is the Mother of Success.
which means Failure is the Mother of Success.
Sometimes this word is translated as prosperity, but success, succeed, or successfully are more correct definitions.
See Also: Prosperity
Naruto
Japanese Anime Series
ナルト is the title “Naruto” from the Japanese animation series. See Naruto Anime Series.
Because of the unique Japanese character set used to write this title, it can only be written by the Japanese master calligrapher. Do not try to order it from one of my Chinese calligraphers.
Please note that while this is the correct title for this anime series, it can also mean the “@” sign or “at” in Japanese under a different context (a Japanese person not familiar with the series may be confused by your wall scroll).
Note: Because this title is entirely Japanese Katakana, it should be written by a Japanese calligrapher.
Seishin-Kai / Seishinkai
聖心会 is the Japanese martial arts title “Seishinkai” or “Seishin-Kai.”
It literally means “Sacred Heart Association” or “Pure-Heart Club.”
聖 can mean holy, sacred, saint, sage, virtuous, expert, wise and good, upright, or correct.
心 can mean heart, mind, center, core, spirit, soul, or vitality.
聖心 creates a word meaning sacred heart, or the holy mind (that of Buddha).
会 in Japanese means association, club, meeting, assembly, party, gathering, conference, athletic meet, or society.
Strong Hearted / Strong Willed
意志堅強 can mean either “strong-hearted,” “strong-willed” or “determination.”
The first two characters can be translated as “will,” “willpower,” “determination,” “volition,” “intention,” or “intent.” But, it should be noted that this first part possesses the element of “heart” in the lower portion of both characters (they also partially carry the meaning “with the whole heart”).
The last two characters mean “strong” or “staunch.”
Chinese word order and grammar are a bit different than English, so in this case, they are in reverse order of English but have the correct meaning in a natural form.
See Also: Strong Willed | Discipline | Will-Power
Kodokan
弘道館 is a Japanese title that romanizes as Kodokan.
There are a few martial arts titles that are romanized as Kodokan, so be careful to choose the correct one. This one kind of means “Great Way Hall.”
In the old Buddhist context, the 弘 Kanji can mean vast, great, to enlarge, spread abroad, or widely to proclaim.
The 道 part is the “Way,” as seen in many martial arts titles. It is the root character of Taoism/Daoism (romanized as Tao or Dao from Chinese, but Do in Japanese).
The 館 or hall part is implied to be a dojo or place of learning.
Ten perfect Mahayana rules
十法 is the title of the ten perfect or perfecting Mahāyāna rules.
The order of rules is as follows:
1. right belief.
2. right conduct.
3. right spirit.
4. the joy of the bodhi mind.
5. joy in the dharma.
6. joy in meditation.
7. pursuing the correct dharma.
8. obedience to, or accordance with dharma.
9. departing from pride, desire, etc.
10. comprehending the inner teaching of Buddha and taking no pleasure in attaining such knowledge or noting the ignorance of others.
This title is only used in the context of Buddhism. Japanese and Chinese people who are not familiar with Buddhism will not recognize this title.
The Saint
聖 is the simple, single-character religious form of “saint” in Chinese (also holds the same meaning in Japanese and Korean, though rarely used alone like this).
This can also mean holy, sage, master, or priest.
Note: 聖 is often used in compound words (words of more than one character) to create further meanings. In compounds, it can mean holy, sacred, or divine.
聖 is also used as the first word for Spanish and English place names such as “San Diego” and “St. Louis” in Chinese (not Japanese).
In the Buddhist context, this can represent ārya or sādhu. And mean a sage; wise and good; upright, or correct in all his character; sacred, holy, or saintly.
Bonsai / Penzai
Dwarf Tree Culture
盆栽 is the word that refers to the culture, hobby, and to miniature trees themselves that have become popular around the world.
Like many things, this art migrated from China to Japan some time ago, but we tend to associate it with Japanese culture and even use the Japanese word in English.
Granted, in the present day, this hobby seems to be more popular in Japan but still has a great following in China and even a little in Korea as well.
Note: Many people confuse the title of the bonsai tree with “banzai” which is a form of “hooray” in Japanese. I have also seen it misspelled as “bansai.” The correct Romanization (Romaji) is “bonsai.”
Five Elements Tai Chi Fist
五行太極拳 is a certain school or style of Tai Chi (Taiji).
The characters literally mean “Five Elements Tai Chi Fist.”
Notes:
In Taiwan, it would be Romanized as “Wu Hsing Tai Chi Chuan” - see the standard Mandarin method above in the gray box (used in mainland China and the official Romanization used by the Library of Congress).
The last three characters are sometimes translated as “Grand Ultimate Fist,” so the whole thing can be “Five Elements Grand Ultimate Fist” if you wish.
I have not confirmed the use of this title in Korean but if it is used, it's probably only by martial arts enthusiasts. The pronunciation is correct, as shown above for Korean.
Live Strong
While hard to translate directly, 堅強生活 is the best way to write “Live Strong” in Chinese. If you are a cancer survivor or support Lance Armstrong's ideas, this is a nice selection for a wall scroll.
The first two characters mean strong or staunch. The last two mean living or life (daily existence). While the Chinese version is the reverse order of “Live Strong” it is the only way to write it in a natural form that is grammatically correct.
Note that we are in no way affiliated or connected to Lance or his foundation. This translation is offered because of multiple requests from customers whose philosophies or ideas match those of the Live Strong idea.
Jin Shin Jyutsu
仁神術 is Jin Shin Jyutsu or Jin Shin Jutsu.
This is a practice of calming the mind and clearing the flow of Qi energy in the body. Jin Shin Jyutsu has some commonality with the practice of Reiki.
A good translation of 仁神術 would be “Benevolent Spirit Method.”
We can break that down into all of the possible meanings:
仁 = benevolence (esp. as a virtue of Confucianism), consideration, compassion, humanity, charity, kindness, or virtue.
神 = deity, soul, spirit, mysterious, psyche, god, divinity, spiritual powers, deva, divine, spiritual, or supernatural.
術 = way, method, means, art, trick, or plan. The correct romaji for this 術 Kanji should be “jutsu.” However, in martial arts, this is often written “jitsu” but in this case, “jyutsu” became common.
This is the most common Chinese character which sounds like “Lee” or “Li” and is used as a surname / family name in China.
李 actually means “Plum.” So it's really Mr. Plum and Mrs. Plum if you translated the name instead of romanizing.
This is not the only character in Chinese that can be romanized as “Lee” or “Li.” If your family name is “Lee” or “Li” please be sure this is the correct character before you order this scroll (look at your grandparents' Chinese passports or other documents if you are an ABC and are trying to create a heritage wall scroll).
Famous people with this surname include Bruce Lee (Li Xiao-Long), Minister Li Peng, and famous Tang Dynasty poet Li Bai.
In Korea, this is the original character for a surname that romanizes as “Yi.”
Note: This also one version of Lee that is a common Korean surname. However, it’s often romanized as "Yi" and sometimes as "Ri" or "Rhee."
Ninja
忍 is just the first character of “Ninja.”
It means to beat, to endure, or to tolerate.
Some use this as the short form of “Ninja” but it would be more correct to use the two-character version in most cases (and for clarity). Other definitions of this Kanji include: to bear, put up with, conceal, spy, or sneak. It is also a character in Korean Hanja and Chinese but not well-known with this meaning but rather a definition like “patience.”![]() Note that when writing this as Kanji, Japanese will tend to write it in the form shown to the right. If you select our Japanese master calligrapher, please expect this Kanji form (yes, it's just one stroke that is slightly different in location, crossing another stroke in the Japanese Kanji form).
Note that when writing this as Kanji, Japanese will tend to write it in the form shown to the right. If you select our Japanese master calligrapher, please expect this Kanji form (yes, it's just one stroke that is slightly different in location, crossing another stroke in the Japanese Kanji form).
Jujitsu / Jujutsu
柔術 has been somewhat incorrectly spelled and pronounced “Jujitsu” for some time in the English-speaking world. The correct Japanese Romaji is Jujutsu or Juujutsu.
A little background on the word: By combining the Kanji pronounced “Ju” (which means flexible, pliable, gentle, yielding) with the Kanji pronounced “Jutsu” (which means art or technique), we get a meaning that can be translated as “flexible technique,” “gentle art” or “yielding technique.”
柔術 does make sense in Chinese as well, although pronounced “rou shu” in China.
The Jujutsu system has a history in Japan that started well before the 1600s. Some see this style as a variation of the “Empty Hand Method” (Karate-do). Even the samurai of old used some Jujutsu methods in defending themselves with their unarmed hands against weapons that could pierce their heavy armor.
There are convoluted relationships between various schools and systems of martial arts, but it's generally accepted that Jujutsu led to the development of Judo and a few other variations.
Devotion / Dedication / Attentive / Focused
專心 makes a word that means “paying attention with your heart.”
It's often translated as “dedication,” as in “be absorbed in” or “concentrate one's efforts.” It's also used to mean “with the single mind,” “whole-heartedly,” “paying attention,” “undivided attention,” “concentration (-ed),” “engrossed,” “devotionally (listening/watching),” and/or “attentive.”
The first character means “for a particular person, occasion, or purpose,” “focused on one single thing,” “concentrated,” and sometimes, “special.”
The second character means “heart” or “mind” by itself.
My favorite translation, which comes from the Oxford Advanced Chinese/English Dictionary, is, “wholehearted devotion.”
If it seems like the meaning of this word is quite open, you are correct. The context in which the word is used matters a lot. It can mean different things depending on how you use it. This makes it kind of nice as you can decide what this means to you (within some limits). This is always positive in meaning, so even if a Chinese person reads it differently than you, it will still have a good meaning.
![]() In Japanese, they tend to use a variation of the second character which has one less stroke. If you want your calligraphy written this Japanese form, please click on the Kanji shown to the right instead of the button above. Note: Japanese and Chinese people will recognize either form.
In Japanese, they tend to use a variation of the second character which has one less stroke. If you want your calligraphy written this Japanese form, please click on the Kanji shown to the right instead of the button above. Note: Japanese and Chinese people will recognize either form.
Justice / Rectitude / Right Decision
Also means: honor loyalty morality righteousness
義 is about doing the right thing or making the right decision, not because it's easy but because it's ethically and morally correct.
No matter the outcome or result, one does not lose face if tempering proper justice.
義 can also be defined as righteousness, justice, morality, honor, or “right conduct.” In a more expanded definition, it can mean loyalty to friends, loyalty to the public good, or patriotism. This idea of loyalty and friendship comes from the fact that you will treat those you are loyal to with morality and justice.
義 is also one of the five tenets of Confucius's doctrine.
![]() There's also an alternate version of this character sometimes seen in Bushido or Korean Taekwondo tenets. It's just the addition of a radical on the left side of the character. If you want this version, click on the image to the right instead of the button above.
There's also an alternate version of this character sometimes seen in Bushido or Korean Taekwondo tenets. It's just the addition of a radical on the left side of the character. If you want this version, click on the image to the right instead of the button above.
This is also a virtue of the Samurai Warrior
See our page with just Code of the Samurai / Bushido here
See Also: Judgment | Impartial | Confucius Tenets
Shogun / Japanese General
将軍 or Shogun, in the simplest definition, is a General, but you could also use words such as commander, lord, overlord, highest ranking, or commanding officer.
The title “Shogun” has held some slightly ambiguous meanings at times in Japanese history.
In the west, when someone mentions “Shogun,” we may be filled with thoughts of gallant warriors. Some might even think of the TV mini-series with Richard Chamberlain. Often westerners use the words, Samurai and Shogun interchangeably, but that's really not technically correct. In the case of the Samurai, the Shogun was a designated (by the emperor) leader of a gild of Samurai. In this context, the Shogun was a Samurai lord. Or effectively, a commanding officer of a company of Samurai - to put it in modern military terms.
Sometimes a Shogun was a general; other times, he was the leader of a military government in Japan - but not a front-line warrior like a Samurai.
Variants of the same characters are used in China for the rank and title of a General of the People's Liberation Army (and the same term and characters have been used for the last 2200 years since the Qin Dynasty).
Sword
劍 is pronounced “jian” in Chinese. When you say it, imagine that you are making the sound of a sword as it clashes with a metal shield. This might get you closer to the correct pronunciation in Chinese.
I actually wonder if this word came from the metallic ringing sounds of a sword in battle - but such knowledge is lost in history.
The sword is a symbol of a warrior. The one thing that a soldier in ancient China lived and died by. A warrior with his skills and sword proves himself of great value. A warrior who losses his sword instantly becomes worthless.
劍 is an excellent scroll for someone in the military (especially officers of all services - as well as enlisted NCO Marines since they still carry swords even if mainly for ceremonial purposes). Or perhaps someone who practices variations of kung fu or tai chi that involve weapons.
Please note that while this character is understood with the sword meaning in Japanese, you might be looking for the word “katana” which also means sword in Japanese but means “knife” in Chinese.
There are other ways to write sword, and here are a few...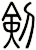
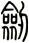
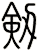
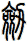
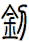


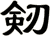

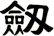
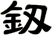



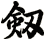
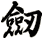
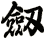
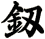






![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

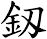
If you are particular about the version you receive, please let me know when you place your order (Note: Special styles are only available from one of our master calligraphers).
Taido
Taidō (The Way of the Body) is a style of Karate practiced in Japan and popular worldwide.
Taidō or 躰道 traces a lineage from Genseiryū (玄制流), which came from Shuri-te (首里手), one of the original martial arts schools of ancient Okinawa.
The first character 躰 is a variant of the original Chinese character 體. In modern Japan, they tend to use 体, a more simple character form. 体 is also the modern Simplified Chinese form of 體.
The 躰 character is correct for this 躰道 martial arts title. But it can be confusing with so many variants out there, not to mention other homophonic Japanese words that also romanize as Taidō or Taidou.
To have a bit more fun with this 躰 character, it has a 身 radical on the left, which sets it apart. The meaning doubles up on the “body” as 身 (shin) is a character that also means body in Japanese and Chinese. On the right is 本, which often means root, stem, origin, source, or fundamental (but can also mean “book” in some contexts). This has deviated from the original 體 which was 骨 (bone) + 豊 (vessel). Hence, the body was your “bone vessel” in ancient Asia.
The meaning of 躰, as well as 體 and 体, is usually translated as the body. When related to the physical body, it can also refer to the torso, trunk, build, physique, or the constitution of a person. As an extension of this, it can also refer to someone's health (good body = good health).
However, depending on the context, it can encompass other meanings such as form, style, system, experience, aspect, corpus, corporeal, substance, or essentials.
The second character, 道, is recognized and well-known as the “Way” and is the same “do” as in Karate-do or Aikido.
Kenjutsu / Kenjitsu
In Japanese, the modern definition, using simple terms, 剣術 is “A martial art involving swords” or “The art of the sword.”
However, in Chinese, this is the word for fencing (as in the Olympic sport).
I will suppose that you want this for the Japanese definition, which comes from skills and techniques developed in the 15th century. At that time, Kenjutsu (or swordsmanship) was a strictly military art taught to Samurai and Bushi (soldiers). The fact that swords are rarely used in military battles anymore, and with the pacification of Japan after WWII, Kenjutsu is strictly a ceremonial practice often studied as a form of martial art (more for the discipline aspect rather than practical purpose).
Language note: The Korean definition is close to the Japanese version described above. However, it should be noted that this can mean “fencing” depending on the context in Japanese, Chinese, and Korean.
![]()
![]() Character variation notes: There are slight variations possible with the second character. Either way is correct and understood by both Japanese and Chinese folks.
Character variation notes: There are slight variations possible with the second character. Either way is correct and understood by both Japanese and Chinese folks.
Since there are about 5 common ways to write the sword character, if you are particular about which version you want, please note that in the “special instructions” when you place your order.
Romanization note: This term is often Romanized as Kenjitsu; however, following the rules of Japanese Romaji, it should be Kenjutsu.
Crisis equals Danger plus Opportunity?
危機 means crisis in Chinese and Japanese.
Separately, the first character here does mean “danger” or “to endanger,” and the second character can mean “opportunity.”
However, I want to debunk a myth that was propagated by some westerners who did not have a clear understanding of Asian languages...
While often, Chinese/Japanese/Korean compound words (words of two or more characters) are the sum of their parts, this is not always the case. The compound is often understood with a completely different meaning than the two characters individually.
Many have said that the Chinese/Japanese/Korean word for Crisis is made up of the characters for “danger” and “opportunity.” 危機 is true when phrased this way.
However, it's not absolutely correct to say that “danger + opportunity = crisis” in Asian cultures.
English example:
If I tell you that...
Bovine creature + Guy behind the plate in baseball = Locomotive train protection
![]()
...you would think I was mad. But consider that “cow + catcher = cowcatcher,” which is the device that used to be found on steam engines to protect them if they hit an animal on the tracks. When we hear the word “cowcatcher,” we don't separate the words into their individual meanings (necessarily).
The same is true with the word for crisis in Chinese/Japanese/Korean. While you can separate the characters, few Asian people would automatically do so in their minds.
The final answer:
It is a half-truth to say, “danger plus opportunity equals crisis” in Chinese/Japanese/Korean. Use this statement and concept with caution.
Also, the second character can mean “secret” or “machine,” depending on context so I guess you have to say “a dangerous machine = crisis” or “danger + a secret = crisis.” Both of these are only slightly more ridiculous than the first premise.
PS: 危機 is probably not a great word for a scroll unless you have a special use for it.
Kenpo / Kempo / Quan Fa / Chuan Fa
拳法 is a form of martial arts that can be translated in several ways.
Some will call it “fist principles,” “the way of the fist,” or even “law of the fist.” The first character literally means fist. The second can mean law, method, way, principle, or Buddhist teaching.
Kempo is really a potluck of martial arts. Often a combination of Chinese martial arts such as Shaolin Kung Fu with Japanese martial arts such as Karate, Jujutsu (Jujitsu), Aikido, and others. You may see the term “Kempo Karate,” which basically means Karate with other disciplines added. In this way, Kempo becomes an adjective rather than a title or school of martial arts.
These facts will long be argued by various masters and students of Kempo. Even the argument as to whether it should be spelled “kenpo” or “Kempo” ensues at dojos around the world (the correct Romaji should actually be “kenpou” if you precisely follow the rules).
The benefit of Kempo is that the techniques are easier to learn and master than pure Kung Fu (wu shu). Students are often taught basic Karate moves, kicks, and punches before augmenting the basic skills with complex Kung Fu techniques. This allows students of Kempo to achieve a level where they can defend themselves or fight in a relatively short amount of time (a few years rather than a decade or more).
Because the definition of this word is so fluid, I should make some notes here:
1. Purists in Okinawa will claim that “Okinawa Kenpo” or “Ryukyu Hon Kenpo” is the original and true version of this martial art from the old kingdom. It is actually little or no connection between Okinawa Kenpo and the way the word is used elsewhere.
2. In Chinese, where these characters are pronounced “quan fa” (sometimes Romanized as “chuan fa” because the Chinese-pinyin “q” actually sounds like an English “ch” sound), these characters do not hold the connotation of being a mixed martial art. It is simply defined as “the law of the fist.”
3. My Japanese dictionary oddly defines Kenpo as the “Chinese art of self-defense.” I personally don't feel this is the most common way that people perceive the word but just something you should know.
Zen / Chan / Meditation
...as in Zen Buddhism
First, let's correct something: The Japanese romanization for this character, “Zen” has penetrated the English language. In English, it's almost always incorrectly used for phrases like “That's so zen.” Nobody says, “That's so meditation” - right? As the title of a sect, this would be like saying, “That's so Baptist!"
禪 by itself just means “meditation.” In that context, it should not be confined to use by any one religion or sect.
Regardless of the dictionary definition, more often than not, this character is associated with Buddhism. And here is one of the main reasons:
Zen is used as the title of a branch of Mahayana Buddhism, which strongly emphasizes meditation practice.
However, it should be noted that Buddhism came from India, and “Chan Buddhism” evolved and developed in medieval China. The Chinese character “Chan” was eventually pronounced as “Zen” in Japanese. Chan Buddhists in China have much in common with Zen Buddhists in Japan.
More about the history of Zen Buddhism here.
Please also note that the Japanese Kanji character for Zen has evolved a little in Japan, and the two boxes (kou) that you see at the top of the right side of the character have been replaced by three dots with tails.
 The original character would still be generally understood and recognized in Japanese (it's considered an ancient version in Japan) but if you want the specifically modern Japanese version, please click on the zen Kanji to the right. Technically, there is no difference between the Tensho and Reisho versions of Zen since they are ancient character styles that existed long before Japan had a written language.
The original character would still be generally understood and recognized in Japanese (it's considered an ancient version in Japan) but if you want the specifically modern Japanese version, please click on the zen Kanji to the right. Technically, there is no difference between the Tensho and Reisho versions of Zen since they are ancient character styles that existed long before Japan had a written language.![]() There is also an alternate/shorthand/simplified Chinese version, which has two dots or tails above the right-side radical. This version is also popular for calligraphy in China. If you want this version, just click the character to the right.
There is also an alternate/shorthand/simplified Chinese version, which has two dots or tails above the right-side radical. This version is also popular for calligraphy in China. If you want this version, just click the character to the right.
Further notes: Zen is just one of seven sects of Buddhism practiced in Japan. The others are 律 Ritsu (or Risshū), 法相 Hossō, 論 Sanron 華嚴 Kegon, 天台 Tendai, and 眞言 Shingon.
Shobo
The correct doctrine of the Buddha
正法 is a Buddhist term that means “True Dharma” or “The true teachings of Buddha.”
Other translations include the just law, proper method, or period of the true law.
These search terms might be related to Correct:
1. Right Understanding / Right Perspective / Right View / Perfect View
2. Right Resolve / Right Thought / Right Intention / Perfect Resolve
3. Right Speech / Right Talk / Perfect Speech
4. Right Action / Perfect Conduct
5. Right Living / Right Livelihood / Perfect Livelihood
6. Right Effort / Right Endeavor / Perfect Effort
7. Right Mindfulness / Right Memory / Perfect Mindfulness
8. Right Concentration / Perfect Concentration
Correct and Proper
Courage to Do What is Right
Do Not Take Action Until the Time is Right
Fix
Fix the Roof Before the Rain; Dig the Well Before You Are Thirsty
Justice / Rectitude / Right Decision
Mark
Mark the Boat to Find the Lost Sword / Ignoring the Changing Circumstances of the World
Mark-Anthony
The following table may be helpful for those studying Chinese or Japanese...
| Title | Characters | Romaji (Romanized Japanese) | Various forms of Romanized Chinese | |
| Correct and Proper | 正確 正确 | seikaku | zhèng què zheng4 que4 zheng que zhengque | cheng ch`üeh chengchüeh cheng chüeh |
| Seichusen | 正中線 | sei chu sen seichusen | ||
| Thibaud | 提博 | tí bó / ti2 bo2 / ti bo / tibo | t`i po / tipo / ti po | |
| Moral Principles Of Life | 人の道 | hitonomichi | ||
| Harimaya | 播磨屋 | harimaya | ||
| Sachi | サチ | sachi | ||
| Miyamoto | 宮本 宫本 | miyamoto | gōng běn / gong1 ben3 / gong ben / gongben | kung pen / kungpen |
| Shaina | 莎爾娜 莎尔娜 | shā ěr nà sha1 er3 na4 sha er na shaerna | sha erh na shaerhna |
|
| Yoshida | 吉田 | Yoshida | ||
| Itosu | 糸洲 | itosu | ||
| Phan | ファン | fan | ||
| Under the Protection of the Dragon Saint | 神龍庇護 神龙庇护 | shén lóng bì hù shen2 long2 bi4 hu4 shen long bi hu shenlongbihu | shen lung pi hu shenlungpihu |
|
| Akari | あかり | akari | ||
| Shugami | 朱紙 | shugami / akagami | ||
| Abundance and Prosperity | 繁榮富裕 繁荣富裕 | hanei yuuhuku haneiyuuhuku hanei yuhuku | fán róng fù yù fan2 rong2 fu4 yu4 fan rong fu yu fanrongfuyu | fan jung fu yü fanjungfuyü |
| Live For The Day | 活在今天 | huó zài jīn tiān huo2 zai4 jin1 tian1 huo zai jin tian huozaijintian | huo tsai chin t`ien huotsaichintien huo tsai chin tien |
|
| 1. Right Understanding Right Perspective Right View Perfect View | 正見 正见 | sei ken / seiken | zhèng jiàn zheng4 jian4 zheng jian zhengjian | cheng chien chengchien |
| Tomika | トミカ | tomika | ||
| Seido Juku | 正道塾 | sei dou juku seidoujuku sei do juku | ||
| Hau | 侯 | hóu / hou2 / hou | ||
| How can you catch tiger cubs without entering the lair of the tiger? | 不入虎穴焉得虎子 | bú rù hǔ xué yān dé hǔ zǐ bu2 ru4 hu3 xue2 yan1 de2 hu3 zi3 bu ru hu xue yan de hu zi buruhuxueyandehuzi | pu ju hu hsüeh yen te hu tzu pujuhuhsüehyentehutzu |
|
| House of Red Delights | 怡紅院 怡红院 | yí hóng yuàn yi2 hong2 yuan4 yi hong yuan yihongyuan | i hung yüan ihungyüan |
|
| Chiu | 邱 | qiū / qiu1 / qiu | ch`iu / chiu | |
| Trust in God In God We Trust | 相信上帝 | xiāng xìn shàng dì xiang1 xin4 shang4 di4 xiang xin shang di xiangxinshangdi | hsiang hsin shang ti hsianghsinshangti |
|
| Kodokan | 光道館 讲道馆 | kou dou kan koudoukan ko do kan | ||
| Yoko Brilliant Glorious | 燿 | you kou / youkou / yo ko | yào / yao4 / yao | |
| Opportunity | 機 机 | hata | jī / ji1 / ji | chi |
| Asian Pride Oriental Pride AZN Pryde | 東方自尊 东方自尊 | tou hou zi son touhouzison to ho zi son | dōng fāng zì zūn dong1 fang1 zi4 zun1 dong fang zi zun dongfangzizun | tung fang tzu tsun tungfangtzutsun |
| Shoshin-Ryu | 正心流 | shou shin ryuu shoushinryuu sho shin ryu | ||
| Success | 成功 | seikou / seiko | chéng gōng cheng2 gong1 cheng gong chenggong | ch`eng kung chengkung cheng kung |
| Naruto | ナルト | na ru to / naruto | ||
| Seishin-Kai Seishinkai | 聖心会 / 聖心會 聖心会 | sei shin kai seishinkai | ||
| Strong Hearted Strong Willed | 意志堅強 意志坚强 | yì zhì jiān qiáng yi4 zhi4 jian1 qiang2 yi zhi jian qiang yizhijianqiang | i chih chien ch`iang ichihchienchiang i chih chien chiang |
|
| Kodokan | 弘道館 | koudoukan / kodokan | ||
| Ten perfect Mahayana rules | 十法 | jippou / jipo | shí fǎ / shi2 fa3 / shi fa / shifa | shih fa / shihfa |
| The Saint | 聖 圣 | sei | shèng / sheng4 / sheng | |
| Bonsai Penzai | 盆栽 | bon sai / bonsai | pén zāi / pen2 zai1 / pen zai / penzai | p`en tsai / pentsai / pen tsai |
| Five Elements Tai Chi Fist | 五行太極拳 五行太极拳 | go gyou tai kyoku ken gogyoutaikyokuken go gyo tai kyoku ken | wǔ xíng tài jí quán wu3 xing2 tai4 ji2 quan2 wu xing tai ji quan wuxingtaijiquan | wu hsing t`ai chi ch`üan wuhsingtaichichüan wu hsing tai chi chüan |
| Live Strong | 堅強生活 坚强生活 | jiān qiáng shēng huó jian1 qiang2 sheng1 huo2 jian qiang sheng huo jianqiangshenghuo | chien ch`iang sheng huo chienchiangshenghuo chien chiang sheng huo |
|
| Jin Shin Jyutsu | 仁神術 | jin shin jutsu jinshinjutsu | rén shén shù ren2 shen2 shu4 ren shen shu renshenshu | jen shen shu jenshenshu |
| Lee | 李 | ri / sumomo | lǐ / li3 / li | |
| Ninja | 忍 | nin | rěn / ren3 / ren | jen |
| Jujitsu Jujutsu | 柔術 柔术 | juu jutsu / juujutsu / ju jutsu | róu shù / rou2 shu4 / rou shu / roushu | jou shu / joushu |
| Devotion Dedication Attentive Focused | 專心 / 専心 / 耑心 专心 | sen shin / senshin | zhuān xīn zhuan1 xin1 zhuan xin zhuanxin | chuan hsin chuanhsin |
| Justice Rectitude Right Decision | 義 义 | gi | yì / yi4 / yi | i |
| Shogun Japanese General | 將軍 将军 | shougun / shogun | jiāng jūn jiang1 jun1 jiang jun jiangjun | chiang chün chiangchün |
| Sword | 劍 剑 | ken / tsurugi | jiàn / jian4 / jian | chien |
| Taido | 躰道 | tai dou / taidou / tai do | ||
| Kenjutsu Kenjitsu | 剣術 剑术 | kenjutsu | jiàn shù / jian4 shu4 / jian shu / jianshu | chien shu / chienshu |
| Crisis equals Danger plus Opportunity? | 危機 危机 | kiki | wēi jī / wei1 ji1 / wei ji / weiji | wei chi / weichi |
| Kenpo Kempo Quan Fa Chuan Fa | 拳法 | kenpou / kenpo | quán fǎ / quan2 fa3 / quan fa / quanfa | ch`üan fa / chüanfa / chüan fa |
| Zen Chan Meditation | 禪 禅 | zen | chán / chan2 / chan | ch`an / chan |
| Shobo | 正法 | shou bou / shoubou / sho bo | zhèng fǎ / zheng4 fa3 / zheng fa / zhengfa | cheng fa / chengfa |
| In some entries above you will see that characters have different versions above and below a line. In these cases, the characters above the line are Traditional Chinese, while the ones below are Simplified Chinese. | ||||
Successful Chinese Character and Japanese Kanji calligraphy searches within the last few hours...
























































