Many custom options...
And formats...

Not what you want?
Try other similar-meaning words, fewer words, or just one word.
Shin Shin in Chinese / Japanese...
Buy a Shin Shin calligraphy wall scroll here!
Personalize your custom “Shin Shin” project by clicking the button next to your favorite “Shin Shin” title below...
2. Keiko Shin
5. Kemo no Shin
10. Spirit / Spiritual Essence
11. Pure Land / Jodo
12. Pure Land Buddhism / Jodo Buddhism
13. Pure Land / Jodo
14. Kenshin-Kan
15. Shintai
18. Shen / Shum
19. Jung Sim Do
20. Nekogami
21. No Mind / Mushin
22. Taido
Jin Shin Jyutsu
仁神術 is Jin Shin Jyutsu or Jin Shin Jutsu.
This is a practice of calming the mind and clearing the flow of Qi energy in the body. Jin Shin Jyutsu has some commonality with the practice of Reiki.
A good translation of 仁神術 would be “Benevolent Spirit Method.”
We can break that down into all of the possible meanings:
仁 = benevolence (esp. as a virtue of Confucianism), consideration, compassion, humanity, charity, kindness, or virtue.
神 = deity, soul, spirit, mysterious, psyche, god, divinity, spiritual powers, deva, divine, spiritual, or supernatural.
術 = way, method, means, art, trick, or plan. The correct romaji for this 術 Kanji should be “jutsu.” However, in martial arts, this is often written “jitsu” but in this case, “jyutsu” became common.
Keiko Shin
Shin Buddhism
True Pure Land Buddhism
浄土真宗 is known in the west as “Shin Buddhism.”
This is a school of Japanese “Pure Land Buddhism.” This form is also known as “True Pure Land Buddhism” or “Jodoshinshu” (jōdoshinshū).
If you are looking for this title, you probably already know the rest of the story.
See Also: Pure Land Buddhism
Shingitai / Shin Gi Tai
心技体 is the Japanese title “shin gi tai” or “shingitai.”
This can refer to the three elements of Sumo wrestlers or martial artists, “heart-technique-physique.”
Here is what each character represents:
心 (shin) mind, heart, and spirit.
技 (gi) skill, knowledge, and experience.
体 (tai) body and physical effort.
心技体 have the same meanings in Chinese, though this title is used much more often in Japanese.
Kemo no Shin
Shin Kakuto-Ryu
Concentration
Chung shin tong il
精神統一 means concentration of mind or mental concentration in old Korean Hanja and Japanese.
This concentration title is one of the 8 Key Concepts of Tang Soo Do.
You'll often see this romanized from Korean as “Chung Shin Tong Il.”
If you want to order the modern Korean Hangul version, click on the Hangul characters in the pronunciation box. Otherwise, this title is valid Korean Hanja (from the 1600 years that Korea used Chinese characters).
Believe / Faith / Trust
śraddhā
信 can mean to believe, truth, faith, fidelity, sincerity, trust, and confidence in Chinese, old Korean Hanja, and Japanese Kanji.
This single character is often part of other words with similar meanings.
It is one of the five basic tenets of Confucius.
In Chinese, it sometimes has the secondary meaning of a letter (as in the mail) depending on context but it will not be read that way when seen on a wall scroll.
In the Buddhist context, this is śraddhā (faith through hearing or being taught).
Heart / Mind / Spirit
心 would often be translated as “heart.”
However, because it was believed in Chinese culture for thousands of years that your consciousness and thoughts came from the big red organ in the middle of your chest, it also means “mind” or “spirit” and sometimes even “soul.”
In Korean, beyond heart, mind, and spirit, this character can mean moral, nature, mind, affections, intentions, core, and center. In fact, it is used in Chinese to mean “center” as well but only with another character in front of it. For instance, “medical center” or even “shopping center.” Separately and alone, it will not be read with that “center” meaning unless thought of as “the center of your soul.”
Spirit / Spiritual Essence
神 is the simplest way to write spirit in Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and old Korean.
This single character alone will conjure up ideas of the spiritual world. 神 can also be translated as “vital awareness” as in the fact that one must know they exist to exist (I think, therefore, I am).
Other translations include:
God, deity, mysterious, divine essence, lively, spiritual being, divinity, supernatural, soul, mind, nerves, and energy. In some extended context, it can mean genius or unusual.
Japanese romanizations vary a lot when this character is combined into other words. However, shin is the original pronunciation taken from Chinese into Japanese. You'll also see it romanized as kami, gami, jin, and a few others, depending on context.
Pure Land / Jodo
浄土 means “Pure Land.”
This term, “Pure Land” is often associated with the Western Pure Land paradise of Amitabha, also known as the “Buddhist paradise.”
浄土 can also be used as an abbreviation for “Pure Land Buddhism.”
You may see this romanized as Jodo, Joudo, or Jōdo. Some also combine Pure Land into Pureland in English.
This can also be a Japanese surname with the same Jodo or Joudo pronunciation.
See Also: Shin Buddhism
Pure Land Buddhism / Jodo Buddhism
浄土宗 is the title of Japanese “Pure Land Buddhism.” This form is also romanized/known as “Jodo Shu” (jōdo shū).
Also known as Amidism for the fact that this is a branch of Mahayana (Mahāyāna) Buddhism which focuses on Amitabha (Amitābha) Buddha. This form of Buddhism, along with Chinese characters, came to Japan via China in the 5th century, according to most historians.
Notes:
Pure Land Buddhism is also known as ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() (jōdo bukkyō).
(jōdo bukkyō).
Some will just express it with just ![]()
![]() (Pure Land).
(Pure Land).
See Also: Shin Buddhism
Pure Land / Jodo
Also a sect of Buddhism
淨土 literally means “pure land” or “clean earth.”
淨土 is also the abbreviated title of a Buddhist sect that involves faith in the rebirth of Buddha Amitabha (Amitābha) in the Western Heaven. Sometimes this sect is translated as “Paradise of the West.” Other titles of this school of Buddhism include Amidism or Elysium.
See Also: Nirvana | Shin Buddhism
Kenshin-Kan
Shintai
In the context of the Japanese Shinto religion, shintai/shin-tai or 神体 is an object of worship believed to contain the spirit of a deity, typically housed in a shrine.
This may not the the Shintai that you are looking for. This is NOT the Shintai massage technique.
身体 (body/health) and 心体 (heart/mind body) also romanize as Shintai. But I don't know what Saul Goodman is referring to as "light body" though the second character should be 体 which means body.
Shinobi / Ninja Outcast
忍び (Shinobi) is a term often associated with ninjas of ancient Japan.
忍び really means stealing (into), a spy, a sneaking thief, stealth, or a surreptitious visit to a house of ill repute. However, 忍び is sometimes used to refer to an outcast ninja.
This term was somehow given a better report when various video games, TV series, and even a movie came out with this Shinobi title.
忍び are sometimes Romanized as two words: Shin obi or Shin-obi.
Note: The first character can be written as 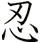 or
or ![]() .
.
Tension and Relaxation
伸縮 can mean, to lengthen and shorten; flexible; adjustable; retractable; extensible; expansion and contraction; elasticity; flexibility; elastic; stretchy.
伸縮 is often romanized from Korean as “Shin Chook,” which is associated with one of the 8 key concepts of Tang Soo Do.
Shen / Shum
Surname
This is a Chinese surname that romanizes as Shen from Mandarin or Shum from Cantonese.
In Japanese, it can be the surnames Chin, Chimu, Sen, Sun, Shin, or Shimu.
The meaning is to sink or heavy.
This 沈 character is a variant of 沉.
Jung Sim Do
This is the Korean martial arts title Jung Sim Do.
The official romanization should be Jeong Sim Do (thought in Korean, the J is almost a "Ch" sound) and other will romanize as Jung Shin Do.
The meaning is straight/right heart way.
If you want this written in Hangul (정심도) in stead of Hanja (正心道), please click on the Hangul characters next to the Korean flag above.
Nekogami
貓神 is the title Nekogami or “Cat God” in Japanese.
This can also be pronounced “neko shin” or “neko kami.”
猫神 is the modern Japanese version, before WWII, this would have been written 貓神 (just the first Kanji varies).
This also makes sense in Chinese, though the traditional version, 貓神, would be better for Chinese calligraphy.
No Mind / Mushin
In Japanese, 無心 means innocent or without knowledge of good and evil. It literally means “without mind.”
無心 is one of the five spirits of the warrior (budo) and is often used as a Japanese martial arts tenet. Under that context, places such as the Budo Dojo define it this way: “No mind, a mind without ego. A mind like a mirror which reflects and dos not judge.” The original term was “mushin no shin,” meaning “mind of no mind.” It is a state of mind without fear, anger, or anxiety. Mushin is often described by the phrase “Mizu no Kokoro,” which means “mind like water.” The phrase is a metaphor describing the pond that clearly reflects its surroundings when calm but whose images are obscured once a pebble is dropped into its waters.
This has a good meaning in conjunction with Chan / Zen Buddhism in Japan. However, out of that context, it means mindlessness or absent-mindedness. To non-Buddhists in China, this is associated with doing something without thinking.
In Korean, this usually means indifference.
Use caution and know your audience before ordering this selection.
More info: Wikipedia: Mushin
Taido
Taidō (The Way of the Body) is a style of Karate practiced in Japan and popular worldwide.
Taidō or 躰道 traces a lineage from Genseiryū (玄制流), which came from Shuri-te (首里手), one of the original martial arts schools of ancient Okinawa.
The first character 躰 is a variant of the original Chinese character 體. In modern Japan, they tend to use 体, a more simple character form. 体 is also the modern Simplified Chinese form of 體.
The 躰 character is correct for this 躰道 martial arts title. But it can be confusing with so many variants out there, not to mention other homophonic Japanese words that also romanize as Taidō or Taidou.
To have a bit more fun with this 躰 character, it has a 身 radical on the left, which sets it apart. The meaning doubles up on the “body” as 身 (shin) is a character that also means body in Japanese and Chinese. On the right is 本, which often means root, stem, origin, source, or fundamental (but can also mean “book” in some contexts). This has deviated from the original 體 which was 骨 (bone) + 豊 (vessel). Hence, the body was your “bone vessel” in ancient Asia.
The meaning of 躰, as well as 體 and 体, is usually translated as the body. When related to the physical body, it can also refer to the torso, trunk, build, physique, or the constitution of a person. As an extension of this, it can also refer to someone's health (good body = good health).
However, depending on the context, it can encompass other meanings such as form, style, system, experience, aspect, corpus, corporeal, substance, or essentials.
The second character, 道, is recognized and well-known as the “Way” and is the same “do” as in Karate-do or Aikido.
Body and Earth in Unity
身土不二 (Shindofuni) is originally a Buddhist concept or proverb referring to the inseparability of body-mind and geographical circumstances.
This reads, “Body [and] earth [are] not two.”
Other translations or matching ideas include:
Body and land are one.
Body and earth can not be separated.
Body earth sensory curation.
You are what you eat.
Indivisibility of the body and the land (because the body is made from food and food is made from the land).
Going further, this speaks of our human bodies and the land from which we get our food being closely connected. This phrase is often used when talking about natural and organic vegetables coming directly from the farm to provide the healthiest foods in Japan.
Character notes: 身(shin) in this context does not just mean your physical body but a concept including both body and mind.
土 (do) refers to the soil, earth, clay, land, or in some cases, locality. It's not the proper name of Earth, the planet. However, it can refer to the land or realm we live in.
Japanese note: This has been used in Japan, on and off, since 1907 as a slogan for a governmental healthy eating campaign (usually pronounced as shindofuji instead of the original shindofuni in this context). It may have been hijacked from Buddhism for this propaganda purpose, but at least this is “healthy propaganda.”
Korean note: The phrase 身土不二 was in use by 1610 A.D. in Korea, where it can be found in an early medical journal.
In modern South Korea, it's written in Hangul as 신토불이. Korea used Chinese characters (same source as Japanese Kanji) as their only written standard form of the language until about a hundred years ago. Therefore, many Koreans will recognize this as a native phrase and concept.
See Also: Strength and Love in Unity
The following table may be helpful for those studying Chinese or Japanese...
| Title | Characters | Romaji (Romanized Japanese) | Various forms of Romanized Chinese | |
| Jin Shin Jyutsu | 仁神術 | jin shin jutsu jinshinjutsu | rén shén shù ren2 shen2 shu4 ren shen shu renshenshu | jen shen shu jenshenshu |
| Keiko Shin | 稽古心 | keiko shin / keikoshin | ||
| Shin Buddhism | 浄土真宗 | jou do shin shuu joudoshinshuu jo do shin shu | ||
| Shingitai Shin Gi Tai | 心技体 | shin gi tai shingitai | xīn jì tǐ xin1 ji4 ti3 xin ji ti xinjiti | hsin chi t`i hsinchiti hsin chi ti |
| Kemo no Shin | 悕望の心 | kemou no shin kemounoshin kemo no shin | ||
| Shin Kakuto-Ryu | 新格闘流 | shin kaku tou ryuu shinkakutouryuu shin kaku to ryu | ||
| Concentration | 精神統一 | seishintouitsu seishintoitsu | ||
| Believe Faith Trust | 信 | shin | xìn / xin4 / xin | hsin |
| Heart Mind Spirit | 心 | kokoro | xīn / xin1 / xin | hsin |
| Spirit Spiritual Essence | 神 | shin / kami | shén / shen2 / shen | |
| Pure Land Jodo | 浄土 | jou do / joudo / jo do | jìng tǔ / jing4 tu3 / jing tu / jingtu | ching t`u / chingtu / ching tu |
| Pure Land Buddhism Jodo Buddhism | 淨土宗 浄土宗 | jou do shuu joudoshuu jo do shu | jìng tǔ zōng jing4 tu3 zong1 jing tu zong jingtuzong | ching t`u tsung chingtutsung ching tu tsung |
| Pure Land Jodo | 淨土 净土 | jou do / joudo / jo do | jìng tǔ / jing4 tu3 / jing tu / jingtu | ching t`u / chingtu / ching tu |
| Kenshin-Kan | 建心館 | ken shin kan kenshinkan | ||
| Shintai | 神体 | shin tai / shintai | ||
| Shinobi Ninja Outcast | 忍び | shino-bi | ||
| Tension and Relaxation | 伸縮 伸缩 | shin shuku / shinshuku | shēn suō / shen1 suo1 / shen suo / shensuo | shen so / shenso |
| Shen Shum | 沈 | jin | shěn / shen3 / shen | |
| Jung Sim Do | 正心道 | zhèng xīn dào zheng4 xin1 dao4 zheng xin dao zhengxindao | cheng hsin tao chenghsintao |
|
| Nekogami | 貓神 猫神 | neko gami / nekogami | māo shén / mao1 shen2 / mao shen / maoshen | |
| No Mind Mushin | 無心 无心 | mu shin / mushin | wú xīn / wu2 xin1 / wu xin / wuxin | wu hsin / wuhsin |
| Taido | 躰道 | tai dou / taidou / tai do | ||
| Body and Earth in Unity | 身土不二 | shindofuni / shindofuji | ||
| In some entries above you will see that characters have different versions above and below a line. In these cases, the characters above the line are Traditional Chinese, while the ones below are Simplified Chinese. | ||||
Successful Chinese Character and Japanese Kanji calligraphy searches within the last few hours...


























