Many custom options...
And formats...

Out in Chinese / Japanese...
Buy an Out calligraphy wall scroll here!
Personalize your custom “Out” project by clicking the button next to your favorite “Out” title below...
1. Respect out of fear is never genuine; Reverence out of respect is never false
2. Chill Out
4. Put out a burning wood cart with a cup of water
5. If you love your child, send them out into the world
6. You are who you hang out with
7. Year-In Year-Out Have Abundance
8. Outstanding
10. Relax
11. Eagle Claw Overturning Fist
12. Lost Love
13. Read / Study
14. The two most important days in your life...
15. Cuong Nhu
16. Gentleness
18. Good Good Study, Day Day Up
20. Midori
21. Kourei
22. Failure is the Mother of Success
24. Wind Wheel
25. Failure is the Mother of Success
26. Snow
28. Lightning
29. Uniform / Complete / Perfect / Order
30. Hiro
31. Release / Let Go
33. No Pain No Gain
34. 1000 good moves ruined by 1 bad
35. Chan
36. Risk / Venture
38. Mark the boat to find the lost sword / Ignoring the changing circumstances of the world
39. Guardian Angel
40. Awareness
43. Eternal Energy / Eternal Matter
44. Hidden Dragon Crouching Tiger
46. Perseverance
47. Nankurunaisa
48. The Karma/Fate/Destiny that Brings Lovers Together
49. Karma
50. Patience / Perseverance / To Endure / Tolerant
51. Adventure
53. Well-Disciplined / Orderly
54. Know Your Enemy, Know Yourself, and You Cannot Lose
55. Three Treasures of Chinese Medicine
56. Mujo no Kaze / Wind of Impermanence
58. Dana: Almsgiving and Generosity
59. Black or white cat matters not as long as it can catch mice
60. Smooth Sailing
61. Fundamental Principles of Tai Chi Chuan
62. Daodejing / Tao Te Ching - Excerpt
63. Holy Bible
64. Kai Zen / Kaizen
65. The Middle Way
67. Nothingness
68. No Mind / Mushin
69. Confucius: Golden Rule / Ethic of Reciprocity
70. An Open Book Benefits Your Mind
71. Banzai / Wansui
72. Listen to Both Sides and be Enlightened, Listen to One Side and be in the Dark
73. Unselfish: Perfectly Impartial
74. A sly rabbit has three openings to its den
75. Gung Ho
76. Banzai
77. Taido
78. Daodejing / Tao Te Ching - Chapter 54
79. Hapkido
Respect out of fear is never genuine; Reverence out of respect is never false
打怕的人是假的敬怕的人是真的 is a proverb that seems to be aimed at world leaders or others in power. Perhaps a suggestion to avoid the practice of “fear-mongering” opting instead for a policy of benevolence and justice.
An example: When the Bush administration told Pakistan they could either join America in the “war on terror,” or expect some bombs to be coming their way, Bush gained this kind of “less-than-genuine respect” from Pakistanis.
Leaders in places like North Korea and even Saudi Arabia reap the same bogus respect from their own citizens.
Note that calligraphers do not like to repeat the same characters in exactly the same way in the same piece of artwork. So expect the characters that are repeated to be written in different forms in the real artwork (unlike the way they are displayed to the left).
Chill Out
There is always a way out
Never say die
Put out a burning wood cart with a cup of water
An utterly inadequate measure
杯水車薪 is a warning against a futile effort.
This proverb literally refers to one who is “trying to put out a burning cart of wood with a cup of water,” or “throw a cup of water on a cartload of wood.” The lesson to be learned is about using the right measure or tool for the job and not wasting your effort if you are inadequately equipped for the task at hand - in other words the postscript should be “go get a bucket or a fire hose.”
If you love your child, send them out into the world
可愛い子には旅をさせよ is a Japanese proverb that means “If you love your children, send them out on a journey into the world.”
This is kind of similar to the western phrase, “Spare the rod and spoil the child.”
More literally, this reads, “Cute child, a journey granted.”
That “granted” could also be understood as “should be initiated.”
Note: Because this selection contains some special Japanese Hiragana characters, it should be written by a Japanese calligrapher.
You are who you hang out with
金似金挨玉似玉 is a Chinese proverb that literally translates as: [One who is] close to gold [is] like gold [and one who is] close to jade [is] like jade.
Figuratively, this means:
A good environment produces good people.
People are influenced by the company they keep.
Basically, if you hang out with good people, you are likely to become or stay good yourself. The opposite also is true. 挨This is like the moral version of “You are what you eat.”
Note: In Japanese, they have a similar phrase, 類は友を呼ぶ (rui wa tomo o yobu) Birds of a feather flock together. However, this is not a good meaning, so we’re not offering it for wall scrolls.
Year-In Year-Out Have Abundance
年年有餘 is a common proverb or wish of prosperity you'll hear around the time of Chinese New Year.
Directly translated character by character, it means “Year Year Have Surplus.” A more natural English translation including the deeper meaning would be “Every Year may you Have Abundance in your life.”
On a side note, this phrase often goes with a gift of something related to fish. This is because the last character, “yu” which means surplus or abundance, has exactly the same pronunciation in Mandarin as the word for “fish.”
This is also one of the most common titles for traditional paintings that feature koi fish.
In China, this phrase might make an odd wall scroll - a customer asked especially for this common phrase which is why it appears here. See my other abundance-related words if you want a wall scroll that will seem more comfortable in Chinese culture.
Note: This can be pronounced in Korean, but it's not a commonly used term.
See Also: Prosperity | Good Fortune
Outstanding
Shinobi / Ninja Outcast
忍び (Shinobi) is a term often associated with ninjas of ancient Japan.
忍び really means stealing (into), a spy, a sneaking thief, stealth, or a surreptitious visit to a house of ill repute. However, 忍び is sometimes used to refer to an outcast ninja.
This term was somehow given a better report when various video games, TV series, and even a movie came out with this Shinobi title.
忍び are sometimes Romanized as two words: Shin obi or Shin-obi.
Note: The first character can be written as 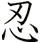 or
or ![]() .
.
Relax
Chill Out
Eagle Claw Overturning Fist
鷹爪翻子拳 is the title of a Chinese martial arts style known as “Ying Zhua Fan Zi Quan” or “Eagle Claw Overturning Fist.”
This style was derived from a combination of 鷹爪派 (Eagle Claw School) and 子母拳 (Son-Mother Fist). The title “son-mother” may seem odd, but it refers to a fist or punches seemingly coming out of another fist or punch. In modern times, 子母彈 is a title for “cluster bomb” (bombs coming out of another bomb).
Lost Love
Read / Study
讀 is a Chinese character that means “to read out loud,” or “to study books.”
Very seldom used in Japanese anymore (except occasionally in Buddhism).
The two most important days in your life...
人生で一番大事な日は二日ある。生まれた日と、なぜ生まれたかを分かった日 is Mark Twain's quote, “The two most important days in your life are the day you are born and the day you find out why” in Japanese.
Note: Because this selection contains some special Japanese Hiragana characters, it should be written by a Japanese calligrapher.
Cuong Nhu
剛柔 is a term that means hardness and softness or hard and soft.
剛柔 is also the Chinese character origin of the martial arts style known as Cương Nhu.
Cương Nhu or Cuong Nhu was founded by Grandmaster Ngo Dong in 1965 in Hue, Vietnam, and brought to the U.S. in 1971.
剛 means hard, firm, strong, and just.
柔 means soft, flexible, supple, yielding, softness, and/or gentleness.
Until it was romanized in the mid-17th century by Portuguese missionaries with later influence by French missionaries, Vietnamese was exclusively written in Chinese characters. With some research, you can still figure out the original way to write most Vietnamese words and titles in Chinese characters. That is what I did here to figure out that Cuong Nhu would have been 剛柔 if established in ancient Vietnam.
Same characters are used in Japanese for various Goju schools of Okinawan martial arts, though not the same lineage as the Vietnamese style described above.
Gentleness
溫柔 or “gentleness” is moving wisely, touching softly, holding carefully, speaking quietly, and thinking kindly.
When you feel mad or hurt, use your self-control. Instead of harming someone, talk things out peacefully. You are making the world a safer, gentler place.
God Give Me Strength
Good Good Study, Day Day Up
好好學習天天向上 is a famous proverb by Chairman Mao Zedong that sounds really strange when directly translated into English.
I include it in our database of phrases to illustrate how different the construction and grammar can be between Chinese and English. The direct translation is “Good Good Study, Day Day Up.” In Chinese, a repeated character/word can often serve to reinforce the idea (like saying “very” or suggesting “a lot of”). So “good good” really means “a lot of good.” While “day day” can be better translated as “day in day out.” The idea of “up” has a meaning in China of “rising above” or “improving.”
After understanding all of this, we come up with a slightly better translation of “With a lot of good study, day in and day out, we raise above.”
The more natural translation of this proverb would be something like, “study hard, and keep improving.”
Endure and Survive
Midori
This can be a Japanese female given name that romanizes as Midori. Note: There are other Kanji combinations that romanize as Midori, this is not the only Midori out there.
Otherwise, and in other Asian languages, this means watercolor.
Kourei
Failure is the Mother of Success
失败是成功之母 is a Chinese and Korean proverb that means “Every failure that you experience is a chance to learn from it and find success.”
Knowing what does not work is just as important as finding out what does work.
See Also: Experience is the Mother of Wisdom
Fortitude / Steadfast
Wind Wheel
Failure is the Mother of Success
失敗は成功の母 is a Japanese proverb that means exactly what you think.
Every failure that you experience is a chance to learn from it and find success.
Knowing what does not work is just as important as finding out what does work.
Note: This is the Japanese version of an ancient Chinese proverb.
Note: Because this selection contains some special Japanese Hiragana characters, it should be written by a Japanese calligrapher.
See Also: Experience is the Mother of Wisdom
Snow
雪 is the Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and old Korean Hanja for the word “snow” or “snowfall.”
Note: In Korean, this can also mean to whiten or wipe out a grievance.
This can also be the female given name “Yuki” in Japanese.
Reality and Illusion
Buddhism Concept
Lightning
Uniform / Complete / Perfect / Order
齊 is a single Chinese character that can mean: neat; even; level with; identical; simultaneous; altogether; to even something out; equal; uniform; complete; perfect; equalize; alike; at the same time; altogether.
齊 is used in the typical Chinese language as well as in Chinese Buddhism. It also has the same meaning in old Korean Hanja.
Chinese Note: This can be Qi or Chi kingdom in China during the Spring and Autumn Period and the Period of the Warring States. It can also be the Chinese surname Qi or Chi.
Japanese Note: In Japanese, this Kanji is usually read as a male given name romanized as Hitoshi (there are other Hitoshi characters) or the Chinese kingdom of Qi / Chi.
it’s
not often understood in Japanese with the same meaning described above. Thus, this character is best if your audience is Chinese.
Hiro
広 is the Japanese variant of 廣 (from Chinese).
The original meaning is wide, numerous, or to spread out. However, in modern Japan, this is used primarily as a given name. Most often it is romanized as Hiro.
This Kanji can also romanize as the names Yutaka, Hiromu, Hiromatsu, Hirotsugu, Hirosue, Hiroji, Hiroshi, Hirosaki, Hirokatsu, Kouji, or Kou.
In Chinese, this would romanize as guǎng where it still holds the original meaning and is a common Chinese surname. However, this 広 version is strictly Japanese, and most Chinese will not realize it’s a variant of 廣. This will be true especially in the mainland where the Simplified Chinese is now written as 广.
Release / Let Go
放 means to release, to free, to let go, to let out, to set off (fireworks).
In Japanese, this can also be a place called Hanashi
放 is also used in the context of Buddhism.
In Buddhism, this can represent the release of desire, materialism, suffering, or mortality.
Return From Death’s Door
絕處逢生 is a Chinese proverb/idiom that talks of coming back from death's door or an unexpected rescue from danger.
Figuratively, this can be to recover from a seemingly impossible situation or to find a way out of a predicament.
If you have survived a near-death experience or severe illness, this might be an appropriate wall scroll for you.
No Pain No Gain
Literally: No Pain, No Strength
1000 good moves ruined by 1 bad
不怕千招会只怕一招熟 is a Chinese proverb that literally translates as: Do not worry about making a thousand clever moves; what [one has to] fear is one bad move.
Figuratively, this means: Even if you have made many clever moves before, one wrong move will ruin the whole game.
I compare this to the English saying, “It takes only one Aw-shit to wipe out a thousand Attaboys.”
Chan
Cantonese Surname
This is the most common Cantonese surname that is often romanized as Chan.
The actual meaning of this character is to lay out, to exhibit, to display, to narrate, to state, to explain, or to tell.
This also can refer to the ancient state of Chan/Chen 1045-479 BC, or the Chen dynasty of China 557-589 BC.
Risk / Venture
風險 is the Chinese word that means risk or venture.
風險 is mostly used in the context of a business venture or the risk you might take on the stock market.
If you like to gamble on the stock market or “let it all hang out” when doing business transactions, this might be the wall scroll for you.
The LORD is my Shepherd
耶和華是我的牧者 is the first line from Psalms 23 straight out of the Chinese Union Bible.
This reads, “The LORD is my shepherd,” or “Jehovah is my shepherd.”
The character breakdown:
耶和華 = Jehovah (most English Bibles translate as LORD or God). This Chinese title is meant to sound a bit like the original Hebrew YHWH or Yahweh.
是 = is.
我的 = my.
牧者 = shepherd.
Mark the boat to find the lost sword / Ignoring the changing circumstances of the world
刻舟求劍 is an originally-Chinese proverb that serves as a warning to people that things are always in a state of change.
Thus, you must consider that and not depend on the old ways or a way that may have worked in the past but is no longer valid.
This idiom/proverb comes from the following story:
A man was traveling in a ferry boat across a river. With him, he carried a treasured sword. Along the way, the man became overwhelmed and intoxicated by the beautiful view and accidentally dropped his prized sword into the river. Thinking quickly, he pulled out a knife and marked on the rail of the boat where exactly he had lost his sword.
When the boat arrived on the other side of the river, the man jumped out of the boat and searched for his sword right under where he'd made the mark. Of course, the boat had moved a great distance since he made the mark, and thus, he could not find the sword.
While this man may seem foolhardy, we must take a great lesson from this parable: Circumstances change, so one should use methods to handle the change. In modern China, this is used in business to mean that one should not depend on old business models for a changing market.
This proverb dates back to the Spring and Autumn period (770–476 BC) of the territory now known as China. It has spread and is somewhat known in Japan and Korea.
Guardian Angel
守護天使 is the title used for guardian angel in Chinese and Japanese Kanji.
It's used in the same way we use this title in the west - such as a guardian angel watching out for you and allowing you to survive a disaster or accident.
The first two characters mean to guard and protect. The second two mean “angel” (literally “Heaven's messenger”).
Awareness
覺 can mean to feel; to figure out; thinking; awake; aware; bodhi; knowing; understanding; enlightenment; illumination; apprehend; perceive; realize.
覺 is a character that is impossible to define in a single word.
This term is often associated with Buddhism where it's understood to be: Illumination, enlightenment, or awakening in regard to the real in contrast to the seeming. However, it can also refer to enlightenment in regard to morality and evil.
Notes:
In Japanese, this can be the personal name Satoru.
In certain context, and only when pronounced as "jiao" in Chinese, it can refer to a nap, sleep or the state of sleeping. However, as a single character on a wall scroll, everyone will read this with the awareness or enlightenment context.
By no means is this the only way to write enlightenment. In fact, you should only choose this character if you are looking more for a word meaning awareness.
See Also: Enlightenment | Wisdom | Knowledge
In Wine there is Truth
酒后吐真言 / 酒後吐真言 is a nice Asian proverb if you know a vintner or wine seller - or wine lover - although the actual meaning might not be exactly what you think or hope.
The literal meaning is that someone drinking wine is more likely to let the truth slip out. It can also be translated as “People speak their true feelings after drinking alcohol.”
It's long believed in many parts of Asia that one can not consciously hold up a facade of lies when getting drunk, and therefore the truth will come out with a few drinks.
I've had the experience where a Korean man would not trust me until I got drunk with him (I was trying to gain access to the black market in North Korea which is tough to do as an untrusted outsider) - so I think this idea is still well-practiced in many Asian countries.
Please note that there are two common ways to write the second character of this phrase. The way it's written will be left up to the mood of the calligrapher, unless you let us know that you have a certain preference.
Shikin Haramitsu Daikomyo
詞韻波羅蜜大光明 are the Japanese Kanji characters that romanize as “Shikin Haramitsu Daikōmyō.”
This is a complicated proverb. I'm actually going to forgo writing any translation information here. You can figure it out via Google search and at sites like Paramita and the Perfection of Wisdom or
Fecastel.Wordpress.com::Shikin Haramitsu Daikōmyō
Eternal Energy / Eternal Matter
不來不去 is a Buddhist term, originally anāgamana-nirgama from Sanskrit.
This implies that things are neither coming into nor going out of existence.
This can also mean “all things are eternal,” or others will call this the Buddhist concept of the eternal conservation of energy.
This theory predates Albert Einstein and Isaac Newton.
Note: 不來不去 is not a well-known word for both Buddhists and non-Buddhists, so not all will recognize it.
The meaning of 藏龍臥虎 is that both the tiger and dragon have amazing talents, but if they are out of view, you may not have discovered them.
This old Chinese idiom/proverb is appropriate for someone with an amazing ability that keeps that ability hidden.
You might think this title is in reverse, but actually, this is the original Chinese proverb.
The movie Crouching Tiger, Hidden Dragon, popularized this alternate version.
Monkey Stealing Peaches
Martial arts term
猴子偷桃 is a martial arts term that I find hilarious. I thought Stephen Chow had made this up for his Monkey King movie. After some research, it turns out to be real.
This can be translated as “monkey stealing peaches” or “monkey steals the peach.” It refers to distracting an opponent with one hand and seizing his testicles with the other.
In colloquial Chinese speech, this can refer to grabbing somebody by the balls (without any martial arts technique to the grabbing).
Perseverance
毅 is the simplest way to express perseverance in Chinese and Korean Hanja.
This single-character version leaves a bit of mystery about what kind of perseverance you might want to convey.
In Korean, this is usually associated with “strength of character.”
In Japanese, this character can be pronounced in a dozen different ways (so we have left out the Japanese pronunciation guide that normally appears above). In Japanese, this Kanji would usually be translated as “strong” (perhaps strong-willed).
Nankurunaisa
Everything will be all right, it will all work out one way or another
なんくるないさ or Nankurunaisa means “Everything will be all right” and/or “It will all work out one way or another.”
なんくるないさ is an Okinawan (琉球 / Ryūkyū Islands) word written in Japanese.
You might see this romanized with breaks like nankurunai-sa or nankuru-nai-sa. It's the same word either way. However, there is a separate word, なんくるない, in there which is nankurunai, translated as “Don't worry, be happy.” The “sa” or さ part indicates an assertion or interjection.
Note: Because this title is entirely Japanese Hiragana, it should be written by a Japanese calligrapher.
The Karma/Fate/Destiny that Brings Lovers Together
姻緣 means “Destiny that brings lovers together.” It can also be translated technically as “Predestined matrimonial affinity” (wow, talk about taking the romance out of this word - that was from the Oxford C-E dictionary).
This speaks to the fate (or karma) that brings a husband and wife together. I would translate this as “Together by fate” or “Joined by destiny” but in the context of marriage. You could use this for non-married lovers, but the first character has a suggestion that this refers to those that are married.
Karma
Single character for Buddhist Karma
This is the simplest way to express the idea of Karma. This is the Buddhist concept of actions committed in a former life affecting the present and future.
Out of the context of Buddhism, this Karma character means one's profession in life, trade, occupation, business, study, or career.
The Karma definition applies to both Chinese and Japanese for this character. This also works as Korean Hanja as Karma; although the meaning can vary depending on context (my Korean dictionary gives the definition of profession/occupation).
See Also: Buddhism
Patience / Perseverance / To Endure / Tolerant
忍耐 is patience, the quiet hope, and trust that things will turn out right.
You wait without complaining. You are tolerant and accepting of difficulties and mistakes. You picture the end in the beginning and persevere to meet your goals.
忍耐 can also mean “to endure,” “restrain oneself,” or “forbearance,” and in some contexts, it can mean “perseverance” or “endurance.”
忍耐 is also used as a tenet of Taekwondo, Tang Soo Do, and other Korean martial arts where it's titled “Endurance” and romanized as “In Neh.”
![]() Note that when writing this as Kanji, Japanese will tend to write the first character in the form shown to the right. If you select our Japanese master calligrapher, please expect this Kanji form (yes,
it’s
just one stroke that is slightly different in location, crossing another stroke in the Japanese Kanji form).
Note that when writing this as Kanji, Japanese will tend to write the first character in the form shown to the right. If you select our Japanese master calligrapher, please expect this Kanji form (yes,
it’s
just one stroke that is slightly different in location, crossing another stroke in the Japanese Kanji form).
See Also: Peace | Harmony | Perseverance
Adventure
If you lead a life of adventure (like I do), a 探險 wall scroll is for you.
Alone, the first character can mean “to explore,” “to search out,” or “to scout.” The second character holds the meanings of “dangerous” and “rugged.” Together these two characters create the word that means “adventure” or “to explore.”
探険 is a modern Japanese Kanji version, but it more precisely means exploration or expedition rather than adventure. 探險 is the old/ancient Japanese version used before WWII. Let us know if you want the modern Japanese version instead.
See Also: Bon Voyage | Travel
Shidai / Sida / Mahabhuta
In Mahayana Buddhism, 四大 represents mahābhūta, the four elements of which all things are made: earth, water, fire, and wind.
This can also represent the four freedoms: speaking out freely, airing views fully, holding great debates, and writing big-character posters.
In some contexts, this can be a university or college offering four-year programs.
To others, this can represent the Tao, Heaven, Earth, and King.
Going back to the Buddhist context, these four elements “earth, water, fire, and wind,” represent 堅, 濕, 煖, 動, which are: solid, liquid, heat, and motion.
Well-Disciplined / Orderly
Special Military Term
When reading an account of some battles in China, I came across the Chinese word, 嚴整. As it turns out, 嚴整 is only used in military circles to describe neat, orderly, and well-disciplined troops. Perhaps this is actually closer to the meaning I was taught while in the U.S. Marines.
The first character literally means stern, serious, strict, or severe (it can also mean airtight or watertight.
The second character means exact, in good order, whole, complete, and orderly.
Together, these two characters multiply each other into a word that expresses the highest military level of discipline.
See Also: Self-Control | Will-Power
Know Your Enemy, Know Yourself, and You Cannot Lose
知彼知己百戰不殆 is from Sun Tzu's (Sunzi's) Art of War. It means that if you know and understand the enemy, you also know yourself, and thus with this complete understanding, you cannot lose.
This proverb is often somewhat directly translated as “Know the enemy and know yourself, and you can fight a hundred battles without defeat.”
It can also be translated as “If you know both yourself and your enemy, you can come out of hundreds of battles without danger,” or “Know your enemy, know yourself, and your victory will not be threatened.”
Three Treasures of Chinese Medicine
精, 氣, 神 are the characters jing, qi, and shen.
As a set, these three characters are known in English as the treasures of traditional Chinese medicine, the treasures of Qi Gong, or the three treasures of Taoism / Daoism.
Sometimes this set is titled 三寶 (sānbǎo) or “three treasures,” but here, we're writing each treasure out.
Here's how these characters are perceived in this context...
Jing: nutritive essence; refined; perfected; pure
Qi: vitality; energy; force; breath; vigor
Shen: spirit; soul; mind; being
To keep it simple, you can use “essence, vitality, and spirit” to define these.
Mujo no Kaze / Wind of Impermanence
無常の風 is an old Japanese proverb that means the wind of impermanence or the wind of change in Japanese.
This can refer to the force that ends life, like the wind scattering a flower's petals. Life is yet another impermanent existence that is fragile, blown out like a candle.
The first two characters mean uncertainty, transiency, impermanence, mutability, variable, and/or changeable.
In some Buddhist contexts, 無常 can be analogous to a spirit departing at death (with a suggestion of the impermanence of life).
The last two characters mean “of wind” or a possessive like “wind of...” but Japanese grammar will have the wind come last in the phrase.
Chen / Chan / Yo / Jin
Surname
This is the most common character for a Chinese surname that romanizes as “Chen.”
This is also a surname You or Yo in Japanese, though it can also be pronounced as Chin in Japanese.
In Korean, it is a surname romanized as Jin.
As a word, this character means: to lay out; to exhibit; to display; to narrate; to state; to explain; to tell.
The Chen clan or family was a small kingdom from 1046 BC to 479 BC. It was one of 12 small-but-powerful vassal states during the Spring and Autumn Period 770-475 BC. This name reappeared as the Chen Dynasty (陳朝) of the Southern dynasties from 557 AD to 589 AD.
Dana: Almsgiving and Generosity
布施 is the Buddhist practice of giving known as Dāna or दान from Pali and Sanskrit.
Depending on the context, this can be alms-giving, acts of charity, or offerings (usually money) to a priest for reading sutras or teachings.
Some will put Dāna in these two categories:
1. The pure or unsullied charity, which looks for no reward here but only in the hereafter.
2. The sullied almsgiving whose object is personal benefit.
The first kind is, of course, the kind that a liberated or enlightened person will pursue.
Others will put Dāna in these categories:
1. Worldly or material gifts.
2. Unworldly or spiritual gifts.
You can also separate Dāna into these three kinds:
1. 財布施 Goods such as money, food, or material items.
2. 法布施 Dharma, as an act to teach or bestow the Buddhist doctrine onto others.
3. 無畏布施 Courage, as an act of facing fear to save someone or when standing up for someone or standing up for righteousness.
The philosophies and categorization of Dāna will vary among various monks, temples, and sects of Buddhism.
Breaking down the characters separately:
布 (sometimes written 佈) means to spread out or announce, but also means cloth. In ancient times, cloth or robs were given to the Buddhist monks annually as a gift of alms - I need to do more research, but I believe there is a relationship here.
施 means to grant, to give, to bestow, to act, to carry out, and by itself can mean Dāna as a single character.
Dāna can also be expressed as 檀那 (pronounced “tán nà” in Mandarin and dan-na or だんな in Japanese). 檀那 is a transliteration of Dāna. However, it has colloquially come to mean some unsavory or unrelated things in Japanese. So, I think 布施 is better for calligraphy on your wall to remind you to practice Dāna daily (or whenever possible).
Black or white cat matters not as long as it can catch mice
Ability is more important than looks
不管黑猫白猫能捉着老鼠的就是好猫 literally translates as: It doesn't matter [if a] cat [is] black [or] white, [as long as it] can catch mice, it's a good cat.
This proverb was either composed or made famous by Deng XiaoPing in 1961 when he exclaimed, “I don't care if it's a white cat or a black cat. It's a good cat so long as it catches mice” when his critics pointed out that his ideas were Capitalistic (free market). The response was meant to say, “It does not matter if it's Communist or Capitalist, as long as it works.”
This is a Chinese proverb that can be used to suggest one should disregard looks or a person's race, as long as they can do the job. It can also be used as a metaphor for many other situations.
Deng XiaoPing probably saved China from collapse (as the Soviet Union experienced). He changed China’s economy from pure Communism to a hybrid where the free market (Capitalism) is encouraged. More about Deng XiaoPing
Smooth Sailing
一帆風順 is just what you think it means. It suggests that you are on a trouble-free voyage through life, or literally on a sailing ship or sailboat. It is often used in China as a wish for good luck on a voyage or as you set out on a new quest or career in your life. Some may use this in place of “bon voyage.”
The literal meaning is “Once you raise your sail, you will get the wind you need, and it will take you where you want to go.” Another way to translate it is “Your sail and the wind follow your will.”
This is a great gift for a mariner, sailor, adventurer, or someone starting a new career.
Note: Can be understood in Korean Hanja but is rarely used.
See Also: Bon Voyage | Adventure | Travel
Fundamental Principles of Tai Chi Chuan
Peng, Lu, Ji, An, Cai, Lie, Zhou, and Kao are the eight fundamentals or forces of Tai Chi Chuan or Taiqiquan.
棚 (Peng) refers to the outward (or upward) expansion of energy.
履 (Lu) is often referred to as “rollback.” Lu is the ability to absorb, yield/deflect incoming force.
擠 (Ji) is often thought of as a “forward press.” However, it is also best described as a “squeezing out of space.”
按 (An) is a downward movement of energy, best translated as “(relaxed) sinking.”
採 (Cai or Tsai) translated as “downward pluck.” Cai is a combination of Lu and An.
列 (Lie or Lieh) is “Split” and is a combination of Peng and Ji.
肘 (Zhou) Elbowing.
靠 (Kao) Shouldering (for when the arms are bound/distance is too close to punch).
Source: https://combativecorner.wordpress.com/2015/12/03/the-8-energies-and-5-movements-of-taijiquan/
Daodejing / Tao Te Ching - Excerpt
Excerpt from Chapter 67
一曰慈二曰儉三曰不敢為天下先 is an excerpt from the 67th Chapter of Lao Tzu's (Lao Zi's) Te-Tao Ching (Dao De Jing).
This is the part where the three treasures are discussed. In English, we'd say these three treasures are compassion, frugality, and humility. Some may translate these as love, moderation, and lack of arrogance. I have also seen them translated as benevolence, modesty, and “Not presuming to be at the forefront in the world.” You can mix them up the way you want, as translation is not really a science but rather an art.
I should also explain that the first two treasures are single-character ideas, yet the third treasure was written out in six characters (there are also some auxiliary characters to number the treasures).
If Lao Tzu's words are important to you, then a wall scroll with this passage might make a great addition to your home.
Holy Bible
聖經 is how to write Bible in Chinese.
The first character means Holy, sacred, saint, or sage.
The second character means sacred book or scripture.
Each Sunday morning, if you are near a Catholic or Protestant Church, you will see plenty of Chinese people carrying their Bibles. Virtually every large or medium city in China has at least one Christian church. Beijing has about 14 Christian churches of Catholic and various Protestant denominations. That number doubles if you count all the church services that are for foreigners only and doubles again if you count all of the underground Christian Churches. Many Embassies (Canadian, Italian, French, etc.) offer Protestant and Catholic services. However, the U.S. Embassy is the most unfriendly in all of China, offering no such religious services, regularly denying entry, and kicking out Americans and others, whether or not they have official business.
Kai Zen / Kaizen
改善 means betterment, improvement, to make better, or to improve - specifically incremental and continuous improvement.
改善 became very important in post-war Japan when Edwards Deming came to Japan to teach concepts of incremental and continuous improvement (for which the big 3 auto-makers did not want to hear about at the time - even kicking Deming out of their offices). The Japanese workforce absorbed this concept when their culture was in flux and primed for change.
This kaizen term is closely associated with the western title “Total Quality Management.” Perhaps dear to my heart since I spent years studying this at university before I moved to China where TQM did not seem to exist. Slowly, this concept has entered China as well (I've actually given lectures on the subject in Beijing).
If you are trying to improve processes at your business or need to remind yourself of your continuous TQM goals, this would be a great wall scroll to hang behind your desk or in your workplace.
See Also: Kansei
The Middle Way
In the most basic translation, 中道 means road through the middle or middle road.
The expanded meaning can be moderation or the golden mean.
But if you are looking for this title, you are probably seeking the Buddhist definition, which is more complex.
中道 is the middle way or middle path of Buddhism. This has various interpretations. In general, it denotes the mean between two extremes and has special reference to the mean between realism and nihilism, or eternal substantial existence and annihilation.
The Buddha teaches that one should not take things to extremes. Don't be extremely evil and engage in debauchery and murder. But do not spend every waking out trying to be a perfect saint. Instead, take the middle path, try to help others, show loving kindness wherever you can, and try not to do harm. If you inadvertently harm another being, make amends if you can, and move on. Realize you are not perfect, but in time, a path of moderation lead toward proper living and enlightenment.
Flying Tigers AVG
飛虎隊 is the full Chinese title of the “Flying Tigers Group.”
These were the American pilots that volunteered to go to China and fight the Japanese before the entry of the USA into World War Two. These fighter pilots were so esteemed in China that fallen American pilots could always find refuge in villages and safe passage and escape to areas of China that were not occupied by Japan at that time. Chinese villagers helped such fallen pilots with full knowledge that when the Japanese occupation forces found out, all the men, women, and children in the village would be massacred by Japanese troops (there are more than a few known cases of such massacres).
The Flying Tigers successfully kept supply lines to the Chinese resistance open and divided Japanese forces at a crucial time while America prepared to join WWII officially.
A wall scroll like this honors the men who risked or gave their lives as noble volunteers and is a reminder of the best moment in the history of Sino-American relations.
These three characters literally mean “flying tiger(s) group/team/squad.”
Note: Hanging these characters on your wall will not make you any friends with Japanese people who are aware or this history (most Japanese have no idea, as Japan’s involvement in WWII has all but been erased from school textbooks in Japan).
Nothingness
空無 is “nothingness” in a Buddhist context.
The first character means empty but can also mean air or sky (air and sky have no form).
The second character means have not, no, none, not, or to lack.
Together these characters reinforce each other into a word that means “absolute nothingness.”
I know this is a term used in Buddhism, but I have not yet figured out the context in which it is used. I suppose it can be the fact that Buddhists believe that the world is a non-real illusion, or perhaps it's about visualizing yourself as “nothing” and therefore leaving behind your desire and worldliness.
Buddhist concepts and titles often have this element of ambiguity or, rather, “mystery.” Therefore, such ideas can have different meanings to different people, and that's okay. If you don't get it right in this lifetime, there will be plenty more lifetimes to master it (whatever “it” is, and if “it” really exists at all).
Soothill defines this as “Unreality, or immateriality, of things, which is defined as nothing existing of independent or self-contained nature.”
No Mind / Mushin
In Japanese, 無心 means innocent or without knowledge of good and evil. It literally means “without mind.”
無心 is one of the five spirits of the warrior (budo) and is often used as a Japanese martial arts tenet. Under that context, places such as the Budo Dojo define it this way: “No mind, a mind without ego. A mind like a mirror which reflects and dos not judge.” The original term was “mushin no shin,” meaning “mind of no mind.” It is a state of mind without fear, anger, or anxiety. Mushin is often described by the phrase “Mizu no Kokoro,” which means “mind like water.” The phrase is a metaphor describing the pond that clearly reflects its surroundings when calm but whose images are obscured once a pebble is dropped into its waters.
This has a good meaning in conjunction with Chan / Zen Buddhism in Japan. However, out of that context, it means mindlessness or absent-mindedness. To non-Buddhists in China, this is associated with doing something without thinking.
In Korean, this usually means indifference.
Use caution and know your audience before ordering this selection.
More info: Wikipedia: Mushin
Confucius: Golden Rule / Ethic of Reciprocity
Do not do to others what you do not want done to yourself
Some may think of this as a “Christian trait,” but actually, it transcends many religions.
This Chinese teaching dates back to about 2,500 years ago in China. Confucius had always taught the belief in being benevolent (ren), but this idea was hard to grasp for some of his students, as benevolence could be kind-heartedness or an essence of humanity itself.
When answering Zhong Gong's question as to what "ren" actually meant, Confucius said:
己所不欲勿施于人 or "When you go out, you should behave as if you were in the presence of a distinguished guest; when people do favors for you, act as if a great sacrifice was made for you. Whatever you wouldn't like done to you, do not do that thing to others. Don't complain at work or home.”
Hearing this, Zhong Gong said humbly, “Although I am not clever, I will do what you say.”
From this encounter, the Chinese version of the “Golden Rule” or “Ethic of Reciprocity” came to be.
The characters you see above express, “Do not do to others whatever you do not want to be done to yourself.”
See Also: Confucius Teachings | Benevolence
An Open Book Benefits Your Mind
There are several ways to translate this ancient proverb. Translated literally and directly, it says, “Open roll has/yields benefit.”
To understand that, you must know a few things...
First, Chinese characters and language have deeper meanings that often are not spoken but are understood - especially with ancient texts like this. Example: It's understood that the “benefit” referred to in this proverb is to the reader's mind. Just the last character expresses that whole idea.
Second, Chinese proverbs are supposed to make you think and leave a bit of mystery to figure out.
Third, for this proverb, it should be noted that roll = book. When this proverb came about (about two thousand years ago), books were rolls of bamboo slips strung together. The first bound books like the ones we use today did not come about until about a thousand years after this proverb when they invented paper in China.
開卷有益 is a great gift for a bookworm who loves to read and increase their knowledge. Or for any friend that is or wants to be well-read.
Some other translations of this phrase:
Opening a book is profitable
The benefits of education.
Banzai / Wansui
Old Japanese / Traditional Chinese & Korean
萬歲 is the traditional Chinese, Korean Hanja, and ancient Japanese way of writing banzai.
In modern times, the first character was simplified in Japan and China. So you might want to select the other entry for universal readability.
While it has become a popular, if not an odd, thing to scream as you jump out of an airplane (preferably with a parachute attached), banzai is actually a very old Asian way to say “hooray.” The Japanese word “banzai” comes from the Chinese word “wan sui,” which means “The age of 10,000 years.” It is actually a wish that the Emperor or the Empire live that long.
Imagine long ago when the Emperor made a rare public appearance. 萬歲 is what all people would yell to their leader in respect.
So if you like it as a hooray, or you want to wish someone that they live for 10,000 years, this is the calligraphy for you.
Other translations include Cheers! (not the drinking kind), hurrah!, long live [name]!, and congratulations!
To other things with banzai in their names, I am still waiting for the promised sequel to Buckaroo Banzai.
Notes: Sometimes people confuse banzai with bonsai. A bonsai is a miniature tree. They have nothing to do with each other.
Listen to Both Sides and be Enlightened, Listen to One Side and be in the Dark
兼聽則明偏聽則暗 is an ancient Chinese proverb about getting all the information from all sides so that you truly understand a situation.

Wei Zheng
A man named Wei Zheng lived between 580-643 AD. He was a noble and wise historian and minister in the court of the early Tang Dynasty. The emperor once asked him, “What should an emperor do to understand the real-world situation, and what makes an emperor out-of-touch with reality?”
Wei Zheng replied, “Listen to both sides and you will be enlightened; listen to only one side and you will be left in the dark.”
Then Wei Zheng went on to cite examples of leaders in history that were victorious after heeding both sides of the story, and other leaders that met their doom because they believed one-sided stories which often came from flattering lips.
Please note that there is an unwritten rule when the same character appears twice in the same phrase, the calligrapher will alter the appearance so that no two characters are exactly alike in the same piece. This calligraphy has two repeating characters that will be written differently than they appear here.
Unselfish: Perfectly Impartial
大公無私 is a Chinese proverb that comes from an old story from some time before 476 BC. About a man named Qi Huangyang, who was commissioned by the king to select the best person for a certain job in the Imperial Court.
Qi Huangyang selected his enemy for the job. The king was very confused by the selection, but Qi Huangyang explained that he was asked to find the best person for the job, not necessarily someone that he liked or had a friendship with.
Later, Confucius commented on how unselfish and impartial Qi Huangyang was by saying, “Da Gong Wu Si” which, if you look it up in a Chinese dictionary, is generally translated as “Unselfish” or “Just and Fair.”
If you translate each character, you'd have something like
“Big/Deep Justice Without Self.”
Direct translations like this leave out a lot of what the Chinese characters really say. Use your imagination, and suddenly you realize that “without self” means “without thinking about yourself in the decision” - together, these two words mean “unselfish.” The first two characters serve to drive the point home that we are talking about a concept that is similar to “blind justice.”
One of my Chinese-English dictionaries translates this simply as “just and fair.” So that is the short and simple version.
Note: This can be pronounced in Korean, but it's not a commonly used term.
See Also: Selflessness | Work Unselfishly for the Common Good | Altruism
A sly rabbit has three openings to its den
-or- The crafty rabbit has three different entrances to its lair
狡兔三窟 speaks to the cunning character of a sly rabbit. Such a rabbit will not have just one hole but rather a few entrances and exits from his liar.
About 2,250 years ago, a rich man told his assistant to go and buy something wonderful that he did not yet possess. He was a man that already had everything, so the assistant went to a local village that owed a great deal of money to the rich man. The assistant told the village elders that all debts were forgiven. All the villagers rejoiced and praised the rich man's name. The assistant returned to the rich man and told him he had purchased “benevolence” for him. The rich man was mildly amused but perhaps slightly confused by the action.
Sometime later, the rich man fell from the favor of the Emperor and was wiped out without a penny to his name. One day he was walking aimlessly and stumbled into the village where the debts had been forgiven. The villagers recognized the man and welcomed him with open arms, clothed, fed him, and gave him a place to live.
Without trying, the man had become like the sly and cunning rabbit. When his exit was blocked, he had another hole to emerge from - and was reborn. This story and idiom come from a book titled “The Amendment” - it's unclear whether this man actually existed or not. But the book did propel this idiom into common use in China.
Still today, this idiom about the rabbit is used in China when suggesting “backup plans,” alternate methods, and anyone with a good escape plan.
Gung Ho
Working Together
工合 is one of those Asian words that is used more in English than in the original Chinese.
Gung Ho was originally used to speak of Carlson's Raiders, a group of “Gung Ho” U.S. Marines who went on an island-hopping campaign of death during WWII.
A movie called Gung Ho came out in the mid-1940s and was later re-released in the 1950s depicting the 2nd Marine Raider Battalion, and brought this word to the mainstream.
It is still sometimes used today within the U.S. Marine Corps brotherhood to refer to a unit or group that works well together or is otherwise efficient and motivated (has good morals).
In 1986, there was a movie called Gung Ho about a Japanese company taking over an American automotive factory. They completely ignored the fact that this was a Chinese title.
It should be noted that this title actually means a condition, state, manner, or the health of something in Japanese.
Language and pronunciation notes:
Like many Asian words absorbed into common use in English, this one is drastically mispronounced. The official Romanization is “gong he” but that doesn't tell you enough. The vowel sound on the first character is like the English word “own,” now just add the g-sounds to the beginning and end. The second character is misleading, as you might think it is like the English word “he.” In reality, the vowel sound is more like the “u” in “up.”
It should also be noted that the current generation in China no longer uses or recognizes this as a common word or slogan.
Note: This can be pronounced and is a word in Japanese, though seldom used. Japanese will use a variation of "具合" instead. But still, not common.
Banzai
Modern Japanese Version
万歲 is the modern Japanese way to write banzai.
We've made two almost identical entries for this word, with just a variation on the first character. In the last century, 萬 was simplified to 万 in Japan and China. The new generation will expect it to be written as 万 but the old generation can still read the more traditional 萬 form. You must make your determination as to what version is best for you. If your audience is mostly Japanese, I suggest 万歲.
While it has become a popular, if not an odd, thing to scream as you jump out of an airplane (preferably with a parachute attached), banzai is actually a very old Asian way to say “hooray.” The Japanese word “banzai” comes from the Chinese word “wan sui” which means “The age of 10,000 years.” It is actually a wish that the Emperor or the Empire live that long.
Imagine long ago when the Emperor made a rare public appearance. This is what all of the people would yell to their leader in respect.
So if you like it as a hooray, or you want to wish someone that they live for 10,000 years, this is the calligraphy for you.
To other things with banzai in their names, I am still waiting for the promised sequel to Buckaroo Banzai.
Other translations: hurrah, long life, congratulations, cheers, live long.
Notes: Sometimes people confuse banzai with bonsai. A bonsai is a miniature tree. They have nothing to do with each other. Further, Bonzai is not a word at all - although it would make a great name for a calcium supplement for older people.
Taido
Taidō (The Way of the Body) is a style of Karate practiced in Japan and popular worldwide.
Taidō or 躰道 traces a lineage from Genseiryū (玄制流), which came from Shuri-te (首里手), one of the original martial arts schools of ancient Okinawa.
The first character 躰 is a variant of the original Chinese character 體. In modern Japan, they tend to use 体, a more simple character form. 体 is also the modern Simplified Chinese form of 體.
The 躰 character is correct for this 躰道 martial arts title. But it can be confusing with so many variants out there, not to mention other homophonic Japanese words that also romanize as Taidō or Taidou.
To have a bit more fun with this 躰 character, it has a 身 radical on the left, which sets it apart. The meaning doubles up on the “body” as 身 (shin) is a character that also means body in Japanese and Chinese. On the right is 本, which often means root, stem, origin, source, or fundamental (but can also mean “book” in some contexts). This has deviated from the original 體 which was 骨 (bone) + 豊 (vessel). Hence, the body was your “bone vessel” in ancient Asia.
The meaning of 躰, as well as 體 and 体, is usually translated as the body. When related to the physical body, it can also refer to the torso, trunk, build, physique, or the constitution of a person. As an extension of this, it can also refer to someone's health (good body = good health).
However, depending on the context, it can encompass other meanings such as form, style, system, experience, aspect, corpus, corporeal, substance, or essentials.
The second character, 道, is recognized and well-known as the “Way” and is the same “do” as in Karate-do or Aikido.
Daodejing / Tao Te Ching - Chapter 54
This is the Mawangdui version of Daodejing chapter 54.
By its virtue alone can one generation after another carry on the ancestral sacrifice.
Apply it to yourself, and by its power, you will be freed from dross.
Apply it to your household, and your household shall thereby have abundance.
Apply it to the village, and the village will be made secure.
Apply it to the kingdom, and the kingdom shall thereby be made to flourish.
Apply it to an empire, and the empire shall thereby be extended.
Therefore just as through oneself, one may contemplate Oneself;
So through the household one may contemplate the Household;
And through the village, one may contemplate the Village;
And through the kingdom, one may contemplate the Kingdom;
And through the empire, one may contemplate the Empire.
How do I know that the empire is so? By this.
What is firmly rooted cannot be pulled out;
What is tightly held in the arms will not slip loose;
Through this, the offering of sacrifice by descendants will never come to an end.
Cultivate it in your person, and its virtue will be genuine;
Cultivate it in the family, and its virtue will be more than sufficient;
Cultivate it in the hamlet, and its virtue will endure;
Cultivate it in the state, and its virtue will abound;
Cultivate it in the empire, and its virtue will be pervasive.
Hence look at the person through the person;
Look at the family through the family;
Look at the hamlet through the hamlet;
Look at the state through the state;
Look at the empire through the empire.
How do I know that the empire is like that?
By means of this.
Hapkido
Korean Martial Art of re-directing force
Hapkido or 合氣道 is a mostly-defensive martial art in Korea.
Hapkido has some connection to the Aikido of Japan. They are written with the same characters in both languages. However, it should be noted that the Korean Hanja characters shown here are the traditional Chinese form - but in modern Japan, the middle character was slightly simplified.
Note: You can consider this to be the older Japanese written form of Aikido. Titles on older books and signs about Aikido use this form.
The connection between Japanese Aikido and Korean Hapkido is muddled in history. The issue is probably due to the difficult relationship between the two countries around WWII. Many Koreans became virtual slaves to the Japanese during that period. After WWII, many things in Korea were disassociated from having any Japanese origin. The relationship has greatly mellowed out now.
Looking at the characters, the first means “union” or “harmony.”
The second character means “universal energy” or “spirit.”
The third means “way” or “method.”
One way to translate this into English is the “Harmonizing Energy Method.” This makes sense, as Hapkido has more to do with redirecting energy than fighting strength against strength.
More Hapkido info
More notes:
1. Sometimes Hapkido is Romanized as “hap ki do,” “hapki-do” “hab gi do” or “hapgido.”
2. Korean Hanja characters are actually Chinese characters that usually hold the same meaning in both languages. There was a time when these characters were the standard and only written form of Korean. The development of modern Korean Hangul characters is a somewhat recent event in the greater scope of history. There was a time when Chinese characters were the written form of many languages in places known in modern times as North Korea, South Korea, Japan, Vietnam, Singapore, Hong Kong, Taiwan, Mainland China, and a significant portion of Malaysia. Even today, more people in the world can read Chinese characters than English.
3. While these Korean Hanja characters can be pronounced in Chinese, this word is not well-known in China and is not considered part of the Chinese lexicon.
Asian Pride / Oriental Pride / AZN Pryde
東方自尊 is the universal way to write “Asian Pride.”
We worked on this one for a long time. The effort involved both Chinese and Japanese translators and lengthy discussions. If you have been searching for this term, there is a reason that it's hard to find the way to write “Asian Pride” in Chinese and Japanese - it's because of the inherent difficulties in figuring out a universal combination of characters that can be read in all languages that use forms of Chinese characters.
This final solution that you see to the left creates a reasonable title in Chinese and an exotic (perhaps unusual) title in Japanese (This could be read as “Eastern Self-Respect” in Japanese”).
Although not as natural, it does have the same meaning as Korean Hanja, and the older generation of Vietnamese people will be able to read it.
The first two characters literally mean “Oriental” and the second two mean “pride,” “self-esteem,” or “self-respect” (we chose the most non-arrogant way to say “pride”). If you have “Asian Pride” (sometimes spelled Asian Pryde) these are the characters for you.
Note: For those who wonder, there is nothing technically wrong with the word “Oriental.” It is a correct word, and any bad meanings were created by so-called “Asian Americans” and Caucasians in the United States. To say “Asian” would not completely correct the intended meaning since that would include people from Saudi Arabia, Iraq, Iran, India, and portions of Russia.
For further proof, if you were of East Asian ancestry and born in England, you would be known as a “British Oriental” (The “Oriental stigma” is basically an American creation and, therefore, applies mainly to the American English language - where they get a bit overzealous with political correctness).
Further, since the Chinese and Japanese word for Oriental is not English, they can not be construed as having ill meaning. On one trip to China or Japan, you will find many things titled with these two characters, such as malls, buildings, and business names. These places also use “Oriental” as their English title (much as we do since our Chinese business name starts with these same two characters).
In short, the first two characters have the meaning that Americans attach to “Asian” but is more technically correct.
This in-stock artwork might be what you are looking for, and ships right away...
Gallery Price: $60.00
Your Price: $36.88
Gallery Price: $60.00
Your Price: $36.88
Gallery Price: $60.00
Your Price: $36.88
Gallery Price: $60.00
Your Price: $36.88
Gallery Price: $60.00
Your Price: $36.88
Gallery Price: $60.00
Your Price: $36.88
Gallery Price: $60.00
Your Price: $36.88
Gallery Price: $60.00
Your Price: $36.88
Gallery Price: $304.00
Your Price: $168.88
Gallery Price: $60.00
Your Price: $36.88
These search terms might be related to Out:
Brought Together From 1000 Miles Away by Fate
Four Noble Truths: Path Leading Away From Suffering
Have a Walking Stick at the Ready Before You Stumble
Lost / Dazed and Confused
Never Put Off Until Tomorrow What You Can Do Today
Nothing is Impossible
Nothing is Impossible With Persistence
The following table may be helpful for those studying Chinese or Japanese...
| Title | Characters | Romaji (Romanized Japanese) | Various forms of Romanized Chinese | |
| Respect out of fear is never genuine; Reverence out of respect is never false | 打怕的人是假的敬怕的人是真的 | dǎ pà de rén shì jiǎ de jìng pà de rén shì zhēn de da3 pa4 de ren2 shi4 jia3 de jing4 pa4 de ren2 shi4 zhen1 de da pa de ren shi jia de jing pa de ren shi zhen de | ta p`a te jen shih chia te ching p`a te jen shih chen te ta pa te jen shih chia te ching pa te jen shih chen te |
|
| Chill Out | 冷静になる | reiseininaru | ||
| There is always a way out | 天無絕人之路 天无绝人之路 | tiān wú jué rén zhī lù tian1 wu2 jue2 ren2 zhi1 lu4 tian wu jue ren zhi lu tianwujuerenzhilu | t`ien wu chüeh jen chih lu tienwuchüehjenchihlu tien wu chüeh jen chih lu |
|
| Put out a burning wood cart with a cup of water | 杯水車薪 杯水车薪 | bēi shuǐ chē xīn bei1 shui3 che1 xin1 bei shui che xin beishuichexin | pei shui ch`e hsin peishuichehsin pei shui che hsin |
|
| If you love your child, send them out into the world | 可愛い子には旅をさせよ | kawaii ko ni wa tabi o sa seyo kawaiikoniwatabiosaseyo kawai ko ni wa tabi o sa seyo | ||
| You are who you hang out with | 挨金似金挨玉似玉 | āi jīn sì jīn āi yù sì yù ai1 jin1 si4 jin1 ai1 yu4 si4 yu4 ai jin si jin ai yu si yu aijinsijinaiyusiyu | ai chin ssu chin ai yü ssu yü aichinssuchinaiyüssuyü |
|
| Year-In Year-Out Have Abundance | 年年有餘 年年有馀 | nián nián yǒu yú nian2 nian2 you3 yu2 nian nian you yu niannianyouyu | nien nien yu yü niennienyuyü |
|
| Outstanding | 出類拔萃 出类拔萃 | chū lèi bá cuì chu1 lei4 ba2 cui4 chu lei ba cui chuleibacui | ch`u lei pa ts`ui chuleipatsui chu lei pa tsui |
|
| Shinobi Ninja Outcast | 忍び | shino-bi | ||
| Relax | 放鬆 放松 | fàng sōng fang4 song1 fang song fangsong | fang sung fangsung |
|
| Eagle Claw Overturning Fist | 鷹爪翻子拳 鹰爪翻子拳 | yīng zhuǎ fān zi quán ying1 zhua3 fan1 zi5 quan2 ying zhua fan zi quan yingzhuafanziquan | ying chua fan tzu ch`üan yingchuafantzuchüan ying chua fan tzu chüan |
|
| Lost Love | 愛迷 | ai mei / aimei | ||
| Read Study | 讀 读 | doku | dú / du2 / du | tu |
| The two most important days in your life... | 人生で一番大事な日は二日ある生まれた日となぜ生まれたかを分かった日 | Jinsei de ichiban daijina hi wa futsuka aru. Umaretahi to, naze umareta ka o wakatta hi | ||
| Cuong Nhu | 剛柔 | gou juu / goujuu / go ju | gāng róu / gang1 rou2 / gang rou / gangrou | kang jou / kangjou |
| Gentleness | 溫柔 温柔 | wēn róu / wen1 rou2 / wen rou / wenrou | wen jou / wenjou | |
| God Give Me Strength | 願上帝給我力量 愿上帝给我力量 | yuàn shàng dì gěi wǒ lì liàng yuan4 shang4 di4 gei3 wo3 li4 liang4 yuan shang di gei wo li liang yuanshangdigeiwoliliang | yüan shang ti kei wo li liang yüanshangtikeiwoliliang |
|
| Good Good Study, Day Day Up | 好好學習天天向上 好好学习天天向上 | hǎo hǎo xué xí tiān tiān xiàng shàng hao3 hao3 xue2 xi2 tian1 tian1 xiang4 shang4 hao hao xue xi tian tian xiang shang | hao hao hsüeh hsi t`ien t`ien hsiang shang hao hao hsüeh hsi tien tien hsiang shang |
|
| Endure and Survive | 凌ぐ | shinogu | ||
| Midori | 水彩 | midori | shuǐ cǎi / shui3 cai3 / shui cai / shuicai | shui ts`ai / shuitsai / shui tsai |
| Kourei | 降霊 | kourei / korei | ||
| Failure is the Mother of Success | 失敗是成功之母 失败是成功之母 | shī bài shì chéng gōng zhī mǔ shi1 bai4 shi4 cheng2 gong1 zhi1 mu3 shi bai shi cheng gong zhi mu shibaishichenggongzhimu | shih pai shih ch`eng kung chih mu shih pai shih cheng kung chih mu |
|
| Fortitude Steadfast | 頑張る | ganbaru | ||
| Wind Wheel | 風輪 风轮 | furin | fēng lún / feng1 lun2 / feng lun / fenglun | |
| Failure is the Mother of Success | 失敗は成功の母 | shippai wa seikou no haha shippaiwaseikounohaha shipai wa seiko no haha | ||
| Snow | 雪 | yuki | xuě / xue3 / xue | hsüeh |
| Reality and Illusion | 真妄 | zhēn wàng zhen1 wang4 zhen wang zhenwang | chen wang chenwang |
|
| Lightning | 閃電 闪电 | shǎn diàn shan3 dian4 shan dian shandian | shan tien shantien |
|
| Uniform Complete Perfect Order | 齊 齐 | hitoshi / hitoshi | qí / qi2 / qi | ch`i / chi |
| Hiro | 広 | hiro | guǎng / guang3 / guang | kuang |
| Release Let Go | 放 | hana / pang | fàng / fang4 / fang | |
| Return From Death’s Door | 絕處逢生 绝处逢生 | jué chǔ féng shēng jue2 chu3 feng2 sheng1 jue chu feng sheng juechufengsheng | chüeh ch`u feng sheng chüehchufengsheng chüeh chu feng sheng |
|
| No Pain No Gain | 不痛不強 不痛不强 | bú tòng bù qiáng bu2 tong4 bu4 qiang2 bu tong bu qiang butongbuqiang | pu t`ung pu ch`iang putungpuchiang pu tung pu chiang |
|
| 1000 good moves ruined by 1 bad | 不怕千招會隻怕一招熟 不怕千招会只怕一招熟 | bú pà qiān zhāo huì zhǐ pà yī zhāo shú bu2 pa4 qian1 zhao1 hui4 zhi3 pa4 yi1 zhao1 shu2 bu pa qian zhao hui zhi pa yi zhao shu | pu p`a ch`ien chao hui chih p`a i chao shu pu pa chien chao hui chih pa i chao shu |
|
| Chan | 陳 陈 | you / yo | chén / chen2 / chen | ch`en / chen |
| Risk Venture | 風險 风险 | fēng xiǎn feng1 xian3 feng xian fengxian | feng hsien fenghsien |
|
| The LORD is my Shepherd | 耶和華是我的牧者 耶和华是我的牧者 | yē hé huá shì wǒ de mù zhě ye1 he2 hua2 shi4 wo3 de mu4 zhe3 ye he hua shi wo de mu zhe yehehuashiwodemuzhe | yeh ho hua shih wo te mu che yehhohuashihwotemuche |
|
| Mark the boat to find the lost sword Ignoring the changing circumstances of the world | 刻舟求劍 刻舟求剑 | kokushuukyuuken kokushukyuken | kè zhōu qiú jiàn ke4 zhou1 qiu2 jian4 ke zhou qiu jian kezhouqiujian | k`o chou ch`iu chien kochouchiuchien ko chou chiu chien |
| Guardian Angel | 守護天使 守护天使 | shu go ten shi shugotenshi | shǒu hù tiān shǐ shou3 hu4 tian1 shi3 shou hu tian shi shouhutianshi | shou hu t`ien shih shouhutienshih shou hu tien shih |
| Awareness | 覺 觉 | gaku / satoru | jué / jiào jue2 / jiao4 jue / jiao jue/jiao | chüeh chiao chüehchiao |
| In Wine there is Truth | 酒后吐真言 / 酒後吐真言 酒后吐真言 | jiǔ hòu tǔ zhēn yán jiu3 hou4 tu3 zhen1 yan2 jiu hou tu zhen yan jiuhoutuzhenyan | chiu hou t`u chen yen chiuhoutuchenyen chiu hou tu chen yen |
|
| Shikin Haramitsu Daikomyo | 詞韻波羅蜜大光明 词韵波罗蜜大光明 | shi kin ha ra mitsu dai kou myo shikinharamitsudaikoumyo shi kin ha ra mitsu dai ko myo | ||
| Eternal Energy Eternal Matter | 不來不去 不来不去 | furai fuko / furaifuko | bù lái bú qù bu4 lai2 bu2 qu4 bu lai bu qu bulaibuqu | pu lai pu ch`ü pulaipuchü pu lai pu chü |
| Hidden Dragon Crouching Tiger | 藏龍臥虎 藏龙卧虎 | cáng lóng wò hǔ cang2 long2 wo4 hu3 cang long wo hu canglongwohu | ts`ang lung wo hu tsanglungwohu tsang lung wo hu |
|
| Monkey Stealing Peaches | 猴子偷桃 | hóu zi tōu táo hou2 zi5 tou1 tao2 hou zi tou tao houzitoutao | hou tzu t`ou t`ao houtzutoutao hou tzu tou tao |
|
| Perseverance | 毅 | see note / seenote / se note | yì / yi4 / yi | i |
| Nankurunaisa | なんくるないさ | nan ku ru nai sa nankurunaisa | ||
| The Karma/Fate/Destiny that Brings Lovers Together | 姻緣 姻缘 | yīn yuán / yin1 yuan2 / yin yuan / yinyuan | yin yüan / yinyüan | |
| Karma | 業 业 | gou / go | yè / ye4 / ye | yeh |
| Patience Perseverance To Endure Tolerant | 忍耐 | nin tai / nintai | rěn nài / ren3 nai4 / ren nai / rennai | jen nai / jennai |
| Adventure | 探險 探险 / 探険 | tanken | tàn xiǎn / tan4 xian3 / tan xian / tanxian | t`an hsien / tanhsien / tan hsien |
| Shidai Sida Mahabhuta | 四大 | shi dai / shidai | sì dà / si4 da4 / si da / sida | ssu ta / ssuta |
| Well-Disciplined Orderly | 嚴整 严整 | yán zhěng yan2 zheng3 yan zheng yanzheng | yen cheng yencheng |
|
| Know Your Enemy, Know Yourself, and You Cannot Lose | 知彼知己百戰不殆 知彼知己百战不殆 | zhí bǐ zhí jī bǎi zhàn bú dài zhi2 bi3 zhi2 ji1 bai3 zhan4 bu2 dai4 zhi bi zhi ji bai zhan bu dai zhibizhijibaizhanbudai | chih pi chih chi pai chan pu tai | |
| Three Treasures of Chinese Medicine | 精氣神 精气神 | jīng qì shén jing1 qi4 shen2 jing qi shen jingqishen | ching ch`i shen chingchishen ching chi shen |
|
| Mujo no Kaze Wind of Impermanence | 無常の風 | mu jou no kaze mujounokaze mu jo no kaze | ||
| Chen Chan Yo Jin | 陳 陈 | chin | chén / chen2 / chen | ch`en / chen |
| Dana: Almsgiving and Generosity | 布施 | fuse | bù shī / bu4 shi1 / bu shi / bushi | pu shih / pushih |
| Black or white cat matters not as long as it can catch mice | 不管黑貓白貓能捉著老鼠的就是好貓 不管黑猫白猫能捉着老鼠的就是好猫 | bù guǎn hēi māo bái māo néng zhuō zhe lǎo shǔ de jiù shì hǎo mǎo bu4 guan3 hei1 mao1 bai2 mao1 neng2 zhuo1 zhe lao3 shu3 de jiu4 shi4 hao3 mao3 bu guan hei mao bai mao neng zhuo zhe lao shu de jiu shi hao mao | pu kuan hei mao pai mao neng cho che lao shu te chiu shih hao mao | |
| Smooth Sailing | 一帆風順 一帆风顺 | yī fán fēng shùn yi1 fan2 feng1 shun4 yi fan feng shun yifanfengshun | i fan feng shun ifanfengshun |
|
| Fundamental Principles of Tai Chi Chuan | 棚履擠按採列肘靠 棚履挤按采列肘靠 | péng lǚ jǐ àn cǎi liè zhǒu kào peng2 lv3 ji3 an4 cai3 lie4 zhou3 kao4 peng lv ji an cai lie zhou kao penglvjiancailiezhoukao | p`eng lü chi an ts`ai lieh chou k`ao peng lü chi an tsai lieh chou kao |
|
| Daodejing Tao Te Ching - Excerpt | 一曰慈二曰儉三曰不敢為天下先 一曰慈二曰俭三曰不敢为天下先 | yī yuē cí èr yuē jiǎn sān yuē bù gǎn wéi tiān xià xiān yi1 yue1 ci2 er4 yue1 jian3 san1 yue1 bu4 gan3 wei2 tian1 xia4 xian1 yi yue ci er yue jian san yue bu gan wei tian xia xian | i yüeh tz`u erh yüeh chien san yüeh pu kan wei t`ien hsia hsien i yüeh tzu erh yüeh chien san yüeh pu kan wei tien hsia hsien |
|
| Holy Bible | 聖經 圣经 | shèng jīng sheng4 jing1 sheng jing shengjing | sheng ching shengching |
|
| Kai Zen Kaizen | 改善 | kai zen / kaizen | gǎi shàn / gai3 shan4 / gai shan / gaishan | kai shan / kaishan |
| The Middle Way | 中道 | chuu dou / chuudou / chu do | zhōng dào zhong1 dao4 zhong dao zhongdao | chung tao chungtao |
| Flying Tigers AVG | 飛虎隊 飞虎队 | fēi hǔ duì fei1 hu3 dui4 fei hu dui feihudui | fei hu tui feihutui |
|
| Nothingness | 空無 空无 | kuu mu / kuumu / ku mu | kōng wú / kong1 wu2 / kong wu / kongwu | k`ung wu / kungwu / kung wu |
| No Mind Mushin | 無心 无心 | mu shin / mushin | wú xīn / wu2 xin1 / wu xin / wuxin | wu hsin / wuhsin |
| Confucius: Golden Rule Ethic of Reciprocity | 己所不欲勿施於人 己所不欲勿施于人 | jǐ suǒ bú yù wù shī yú rén ji3 suo3 bu2 yu4, wu4 shi1 yu2 ren2 ji suo bu yu, wu shi yu ren jisuobuyu,wushiyuren | chi so pu yü, wu shih yü jen chisopuyü,wushihyüjen |
|
| An Open Book Benefits Your Mind | 開卷有益 开卷有益 | kāi juàn yǒu yì kai1 juan4 you3 yi4 kai juan you yi kaijuanyouyi | k`ai chüan yu i kaichüanyui kai chüan yu i |
|
| Banzai Wansui | 萬歲 万岁 | banzai / manzai | wàn suì / wan4 sui4 / wan sui / wansui | |
| Listen to Both Sides and be Enlightened, Listen to One Side and be in the Dark | 兼聽則明偏聽則暗 兼听则明偏听则暗 | jiān tīng zé míng, piān tīng zé àn jian1 ting1 ze2 ming2, pian1 ting1 ze2 an4 jian ting ze ming, pian ting ze an | chien t`ing tse ming, p`ien t`ing tse an chien ting tse ming, pien ting tse an |
|
| Unselfish: Perfectly Impartial | 大公無私 大公无私 | dà gōng wú sī da4 gong1 wu2 si1 da gong wu si dagongwusi | ta kung wu ssu takungwussu |
|
| A sly rabbit has three openings to its den | 狡兔三窟 | jiǎo tù sān kū jiao3 tu4 san1 ku1 jiao tu san ku jiaotusanku | chiao t`u san k`u chiaotusanku chiao tu san ku |
|
| Gung Ho | 工合 | guai | gōng hé / gong1 he2 / gong he / gonghe | kung ho / kungho |
| Banzai | 万歲 / 萬歲 万岁 | banzai | wàn suì / wan4 sui4 / wan sui / wansui | |
| Taido | 躰道 | tai dou / taidou / tai do | ||
| Daodejing Tao Te Ching - Chapter 54 | 善建者不拔善抱者不脫子孫以祭祀不絕修之身其德乃真修之家其德有余修之鄉其德乃長修之國其德乃夆修之於天下其德乃博以身觀身以家觀家以鄉觀鄉以邦觀邦以天下觀天下吾何以知天下然茲以此 善建者不拔善抱者不脱子孙以祭祀不绝修之身其德乃真修之家其德有余修之乡其德乃长修之国其德乃夆修之于天下其德乃博以身观身以家观家以乡观乡以邦观邦以天下观天下吾何以知天下然兹以此 | shàn jiàn zhě bù bá shàn bào zhě bù tuō zǐ sūn yǐ jì sì bù jué xiū zhī shēn qí dé nǎi zhēn xiū zhī jiā qí dé yǒu yú xiū zhī xiāng qí dé nǎi zhǎng xiū zhī guó qí dé nǎi féng xiū zhī yú tiān xià qí dé nǎi bó yǐ shēn guān shēn yǐ jiā guān jiā yǐ xiāng guān xiāng yǐ bāng guān bāng yǐ tiān xià guān tiān xià wú hé yǐ zhī tiān xià rán zī yǐ cǐ shan4 jian4 zhe3 bu4 ba2 shan4 bao4 zhe3 bu4 tuo1 zi3 sun1 yi3 ji4 si4 bu4 jue2 xiu1 zhi1 shen1 qi2 de2 nai3 zhen1 xiu1 zhi1 jia1 qi2 de2 you3 yu2 xiu1 zhi1 xiang1 qi2 de2 nai3 zhang3 xiu1 zhi1 guo2 qi2 de2 nai3 feng2 xiu1 zhi1 yu2 tian1 xia4 qi2 de2 nai3 bo2 yi3 shen1 guan1 shen1 yi3 jia1 guan1 jia1 yi3 xiang1 guan1 xiang1 yi3 bang1 guan1 bang1 yi3 tian1 xia4 guan1 tian1 xia4 wu2 he2 yi3 zhi1 tian1 xia4 ran2 zi1 yi3 ci3 shan jian zhe bu ba shan bao zhe bu tuo zi sun yi ji si bu jue xiu zhi shen qi de nai zhen xiu zhi jia qi de you yu xiu zhi xiang qi de nai zhang xiu zhi guo qi de nai feng xiu zhi yu tian xia qi de nai bo yi shen guan shen yi jia guan jia yi xiang guan xiang yi bang guan bang yi tian xia guan tian xia wu he yi zhi tian xia ran zi yi ci | shan chien che pu pa shan pao che pu t`o tzu sun i chi ssu pu chüeh hsiu chih shen ch`i te nai chen hsiu chih chia ch`i te yu yü hsiu chih hsiang ch`i te nai chang hsiu chih kuo ch`i te nai feng hsiu chih yü t`ien hsia ch`i te nai po i shen kuan shen i chia kuan chia i hsiang kuan hsiang i pang kuan pang i t`ien hsia kuan t`ien hsia wu ho i chih t`ien hsia jan tzu i tz`u shan chien che pu pa shan pao che pu to tzu sun i chi ssu pu chüeh hsiu chih shen chi te nai chen hsiu chih chia chi te yu yü hsiu chih hsiang chi te nai chang hsiu chih kuo chi te nai feng hsiu chih yü tien hsia chi te nai po i shen kuan shen i chia kuan chia i hsiang kuan hsiang i pang kuan pang i tien hsia kuan tien hsia wu ho i chih tien hsia jan tzu i tzu |
|
| Hapkido | 合氣道 合气道 | ai ki do / aikido | hé qì dào he2 qi4 dao4 he qi dao heqidao | ho ch`i tao hochitao ho chi tao |
| Asian Pride Oriental Pride AZN Pryde | 東方自尊 东方自尊 | tou hou zi son touhouzison to ho zi son | dōng fāng zì zūn dong1 fang1 zi4 zun1 dong fang zi zun dongfangzizun | tung fang tzu tsun tungfangtzutsun |
| In some entries above you will see that characters have different versions above and below a line. In these cases, the characters above the line are Traditional Chinese, while the ones below are Simplified Chinese. | ||||
Successful Chinese Character and Japanese Kanji calligraphy searches within the last few hours...

































































































